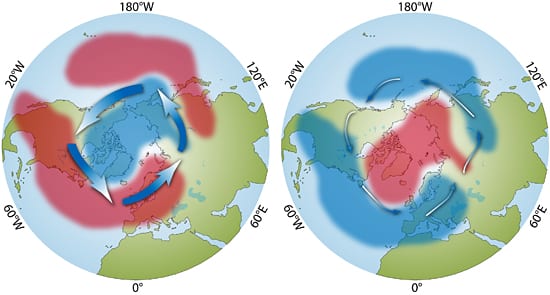
The severity of wintertime climate over North America and Europe is strongly linked to the most prominent atmospheric pattern in the Northern Hemisphere, a seesaw exchange of air massed called the “northern annular mode.” This mode is a natural shift of air masses back and forth between the North Pole and mid-latitudes. At some times (left), a surplus of air mass and pressure (blue) exists over the pole and a deficit (red) exists at around 45°N; at other times (right), the air mass is redistributed to create a deficit at the pole and a surplus in mid-latitudes. This seesaw exchange of air masses shifts wind patterns (blue arrows), as well as temperature and storm conditions. (Illustration by E. Paul Oberlander, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
Image and Visual Licensing
WHOI copyright digital assets (stills and video) on this website can be licensed for non-commercial use upon request and approval. Please submit your request via our Media Request Form.
For assistance or accessibility accommodations, call (508) 289-2647.