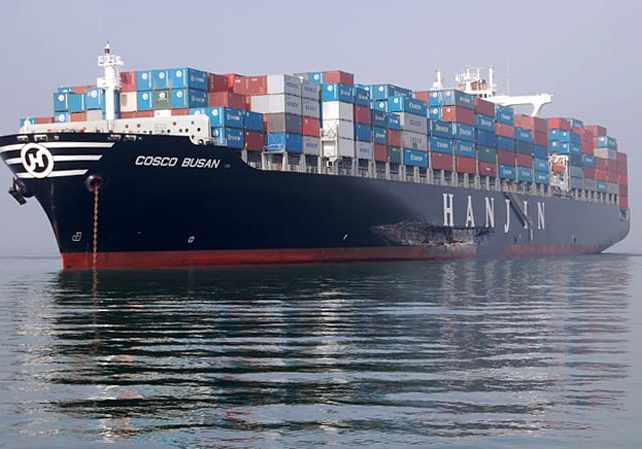
2007 M/V Cosco Busan
Location: San Francisco Bay
Date: November 7, 2007
Lat./Long.: 37°48'29.30"N, 122°23'8.06"W
Material spilled: Bunker fuel
Amount spilled: approx. 53,500 gallons
Spill extent: 150 sq. miles; 26 miles of shoreline
On November 7, 2007, the container ship M/V Cosco Busan struck the San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge, opening a roughly 100-foot gash in the hull that ruptured rupturing three tanks: two containing fuel for transport and one ballast tank Approximately 53,500 gallons of heavy fuel oil (HFO), or bunker oil, leaked into San Francisco Bay, impacting nearly 120 miles of coastline.
Heavy fuel oils are widely used to power marine vessels there have only been a few well-studied HFO spills. These fuels are different from other fuels (e.g., diesel and gasoline) in that they are made from the residue left behind after the distillation of crude oil distillation by adding cutting oils to decrease viscosity. Because both crude oils and cutting oils vary, there is no standard composition for HFOs and understanding how this variability in composition affects weathering is crucial to predicting impacts of future spills.