Alvin‘s Animals
Species named for Alvin pilots
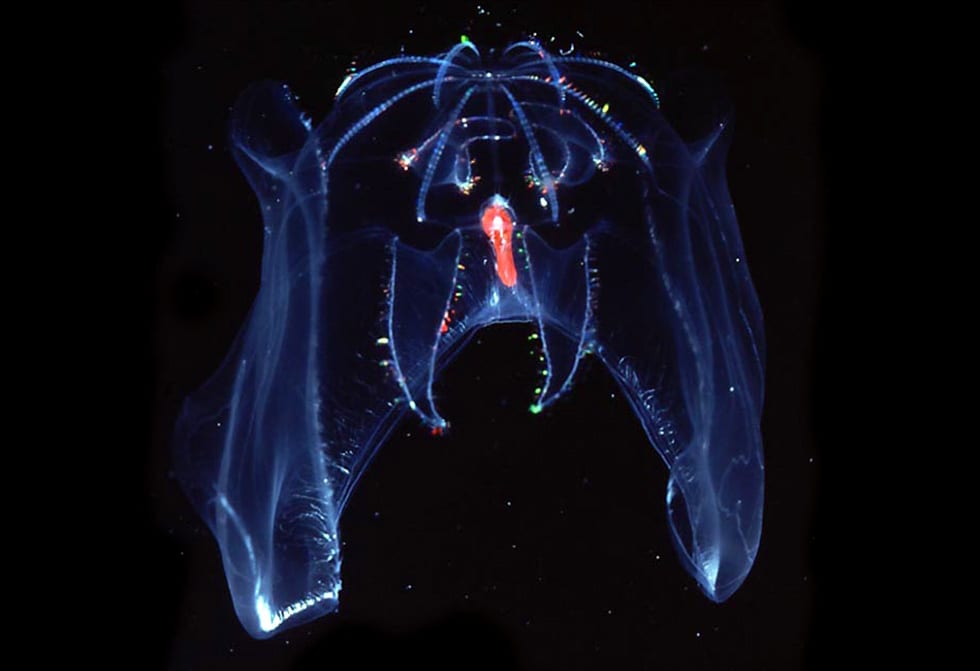
In 1979, pilot Dudley Foster used a “slurp gun” suction sampler to capture a fragile, transparent jelly-animal at midwater depths of about 3,280 feet: Bathocyroe fosteri.
(Larry Madin/WHOI)Species named for Alvin pilots
In 1988, pilot Ralph Hollis used a net held in Alvin’s manipulator arm to capture a purple fish seen near hydrothermal vents: Bythites hollisi.
(WHOI Advanced Imaging and Visualization Laboratory)Species named for Alvin pilots
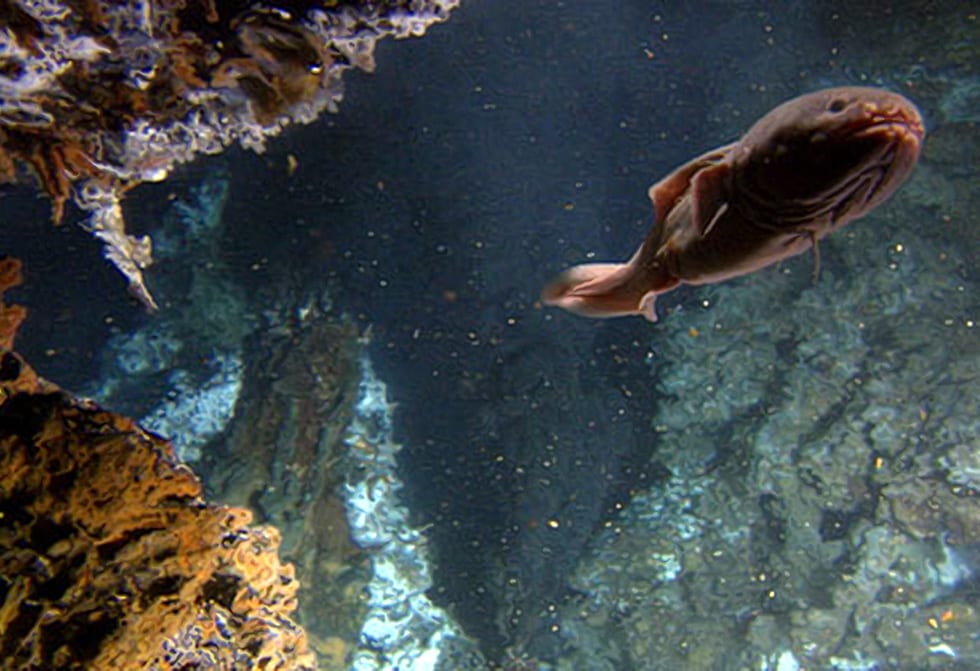
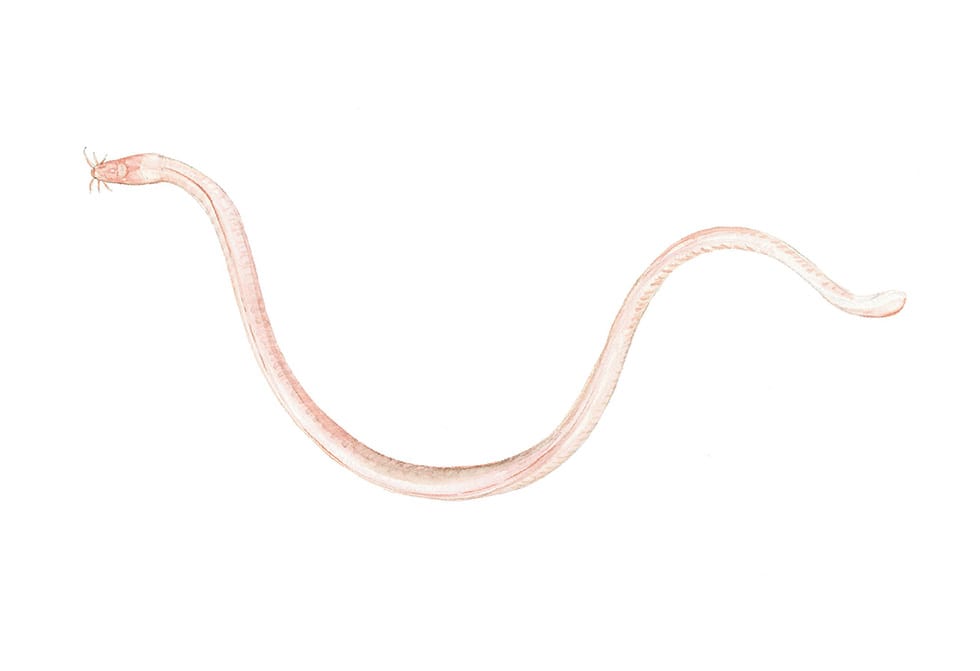
In 2005, pilot Bruce Strickrott captured an eel-like hagfish with a suction sampler: Eptatretus strickrotti.
(Karen Jacobsen/Marine Biological Laboratory)Species named for Alvin itself
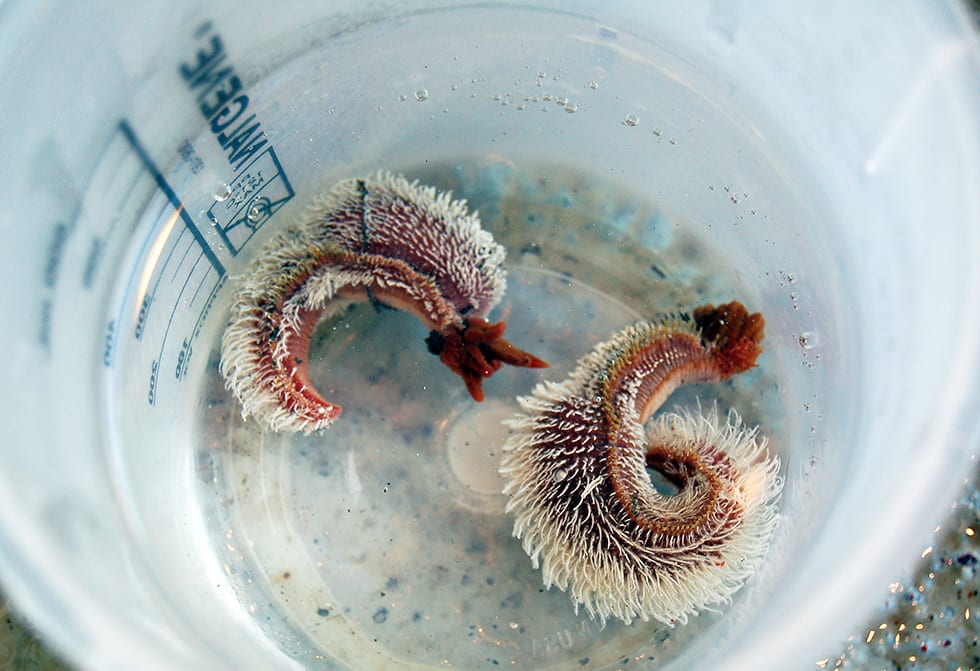
The “Pompeii worm” (Alvinella pompejana) is a furry worm with red tentacles that can withstand the hottest temperatures of any animal, even short periods at 130°F (55°C).
(Irene Garcia-Berdeal/WHOI)Species named for Alvin itself
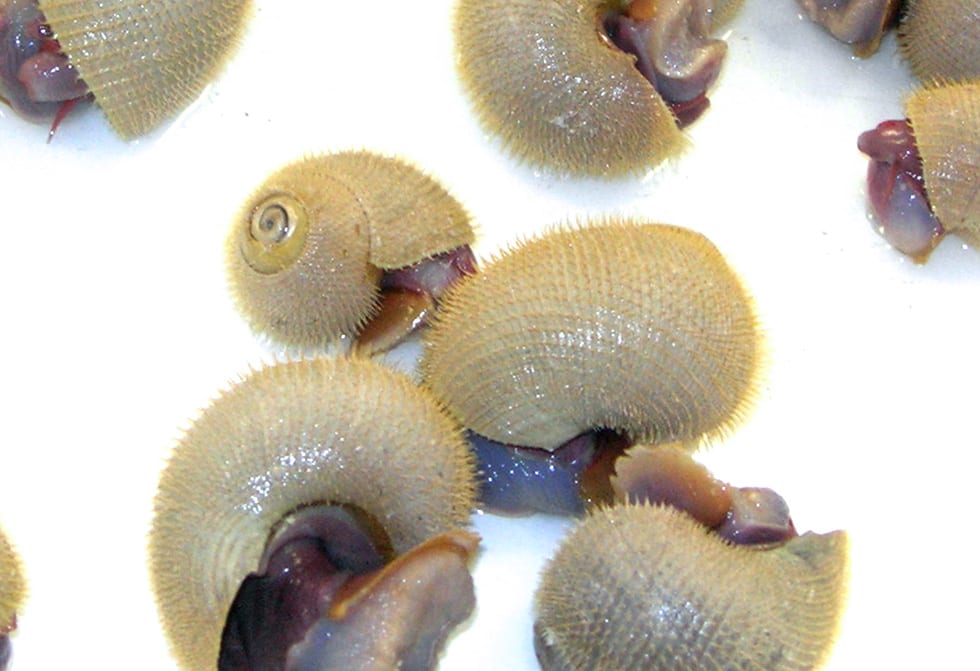
Furry vent snails (Alvinoconcha hessleri) have hair-like projections all over their shells.
(Tom Bolmer/WHOI)Close encounters with Alvin
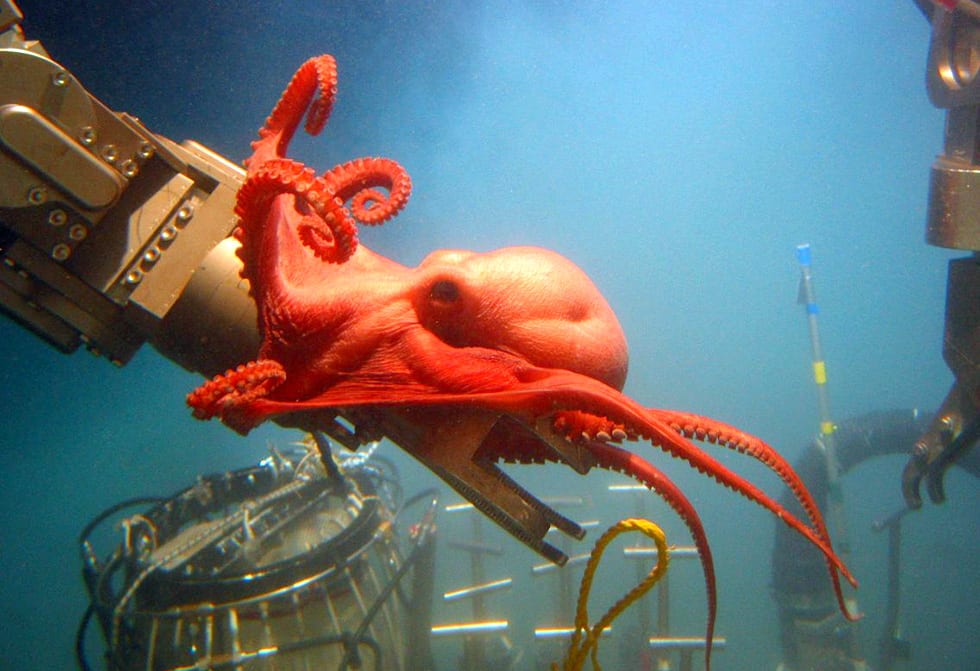
A big red octopus grabbed onto Alvin’s arm at 7,500 feet deep and was discovered to be a new species (Benthoctopus sp.).
(Bruce Strickrott/WHOI)Close encounters with Alvin
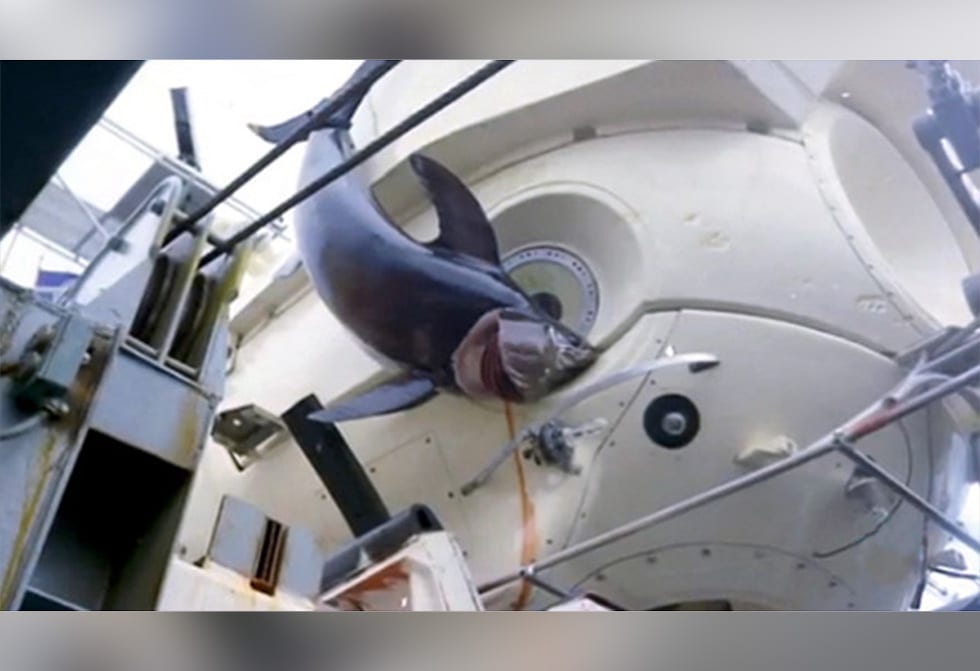
In 1967, a swordfish attacked Alvin at 2,000 feet down, became stuck in the sub’s skin, and was brought to the surface with Alvin (and later eaten for dinner).
(WHOI Archives)Six iconic animals from Alvin’s visits to seafloor vents
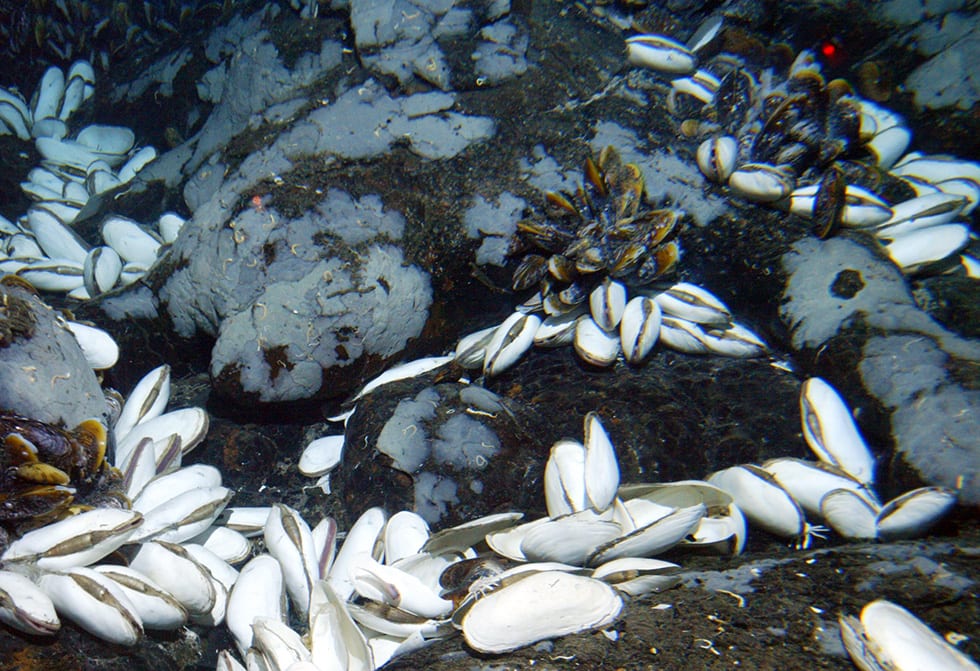
Scientists were astonished to see huge clams living at a depth where they thought no large life could exist. The giant white vent clams (Calyptogena magnifica), reaching up to a foot long, were first seen in 1977 at the Galápagos Rift in the Pacific Ocean.
(WHOI)Six iconic animals from Alvin’s visits to seafloor vents
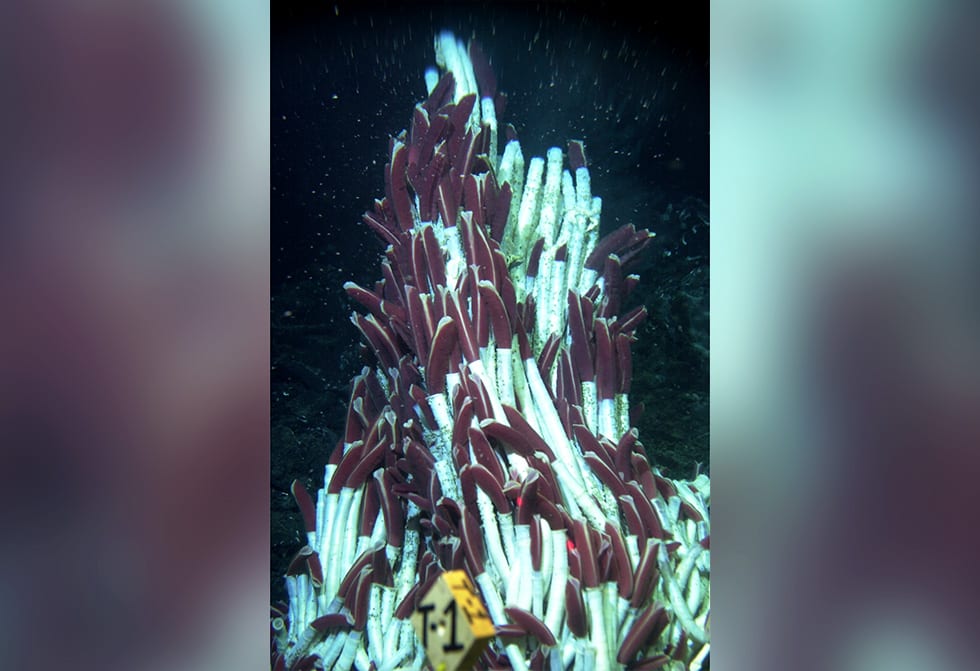
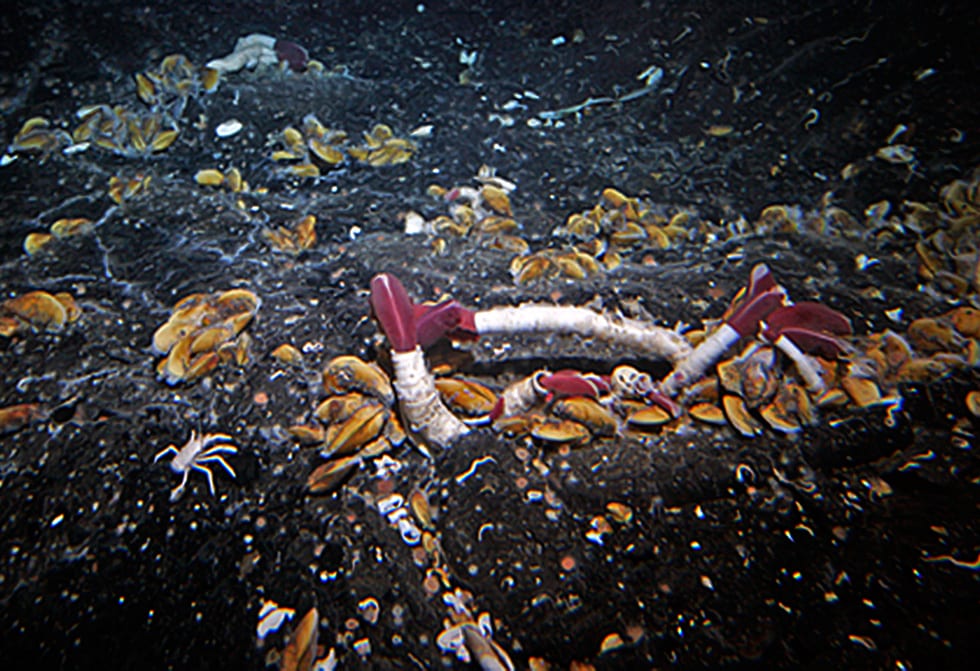
Alvin also found dense groves of six-foot-long red-and-white tubeworms (Riftia pachyptila) at Galápagos Rift vents, growing near vent fluid laden with toxic chemicals. With no mouth or digestive system, the worms provide a steady supply of chemicals to masses of bacteria living inside them. The bacteria use the chemicals for energy and nourish the worms.
(WHOI Archives)Six iconic animals from Alvin’s visits to seafloor vents
At the Galápagos vents, scientists in Alvin saw big brown mussels (Bathymodiolus thermophilus). Like tubeworms, clams, and many other vent animals, the mussels harbor endosymbiotic bacteria, but they also have a digestive system and can catch and eat prey.
(WHOI)Six iconic animals from Alvin’s visits to seafloor vents
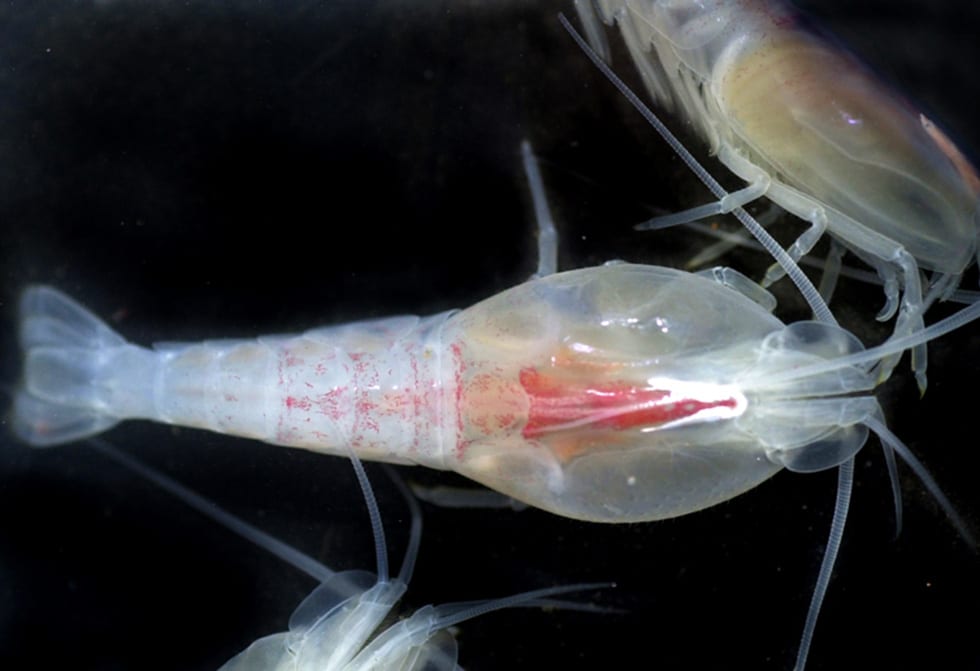
In 1986, scientists in Alvin found a new kind of shrimp swarming around vents on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The shrimp (Rimicaris exoculata) have no eyes, but they have a big spot of visual pigment on their backs. Scientists think the spot can detect faint radiation given off by the super-hot vents, helping the shrimp avoid being parboiled.
(é Ifremer-Victor/Campagne Serpentine 2007)Six iconic animals from Alvin’s visits to seafloor vents
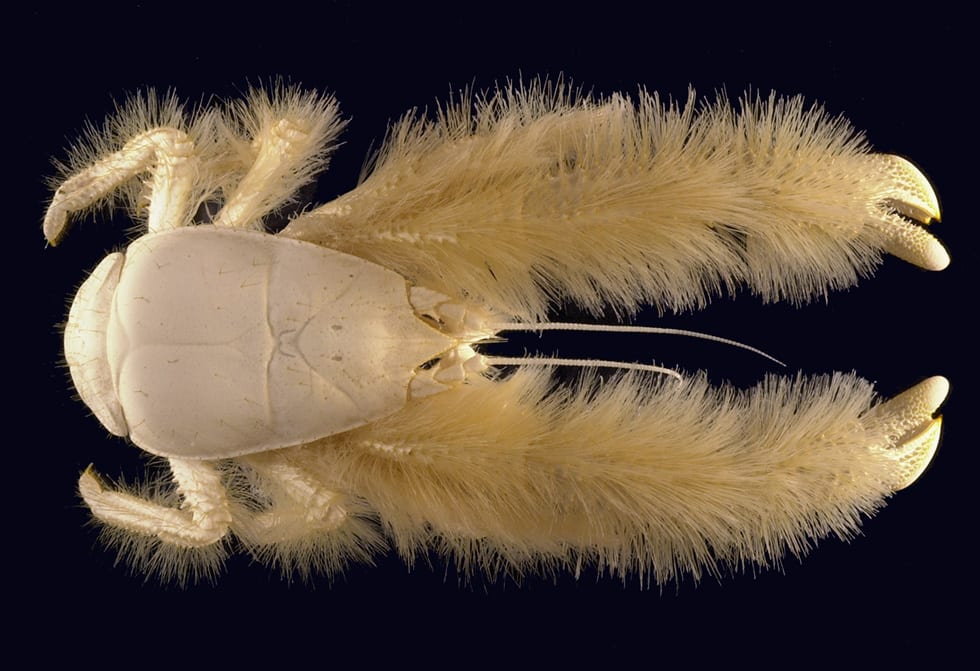
Many crab species live at hydrothermal vents, scavenging and eating other organisms. In 2005 scientists in Alvin discovered these big white crabs with long “fur” on their legs. They are called Kiwa hirsuta. But their nickname is “Yeti crab,” after the fictional “abominable snowman.” This image comes to us courtesy of The Institute Ifremer.
(Courtesy M. Segonzac (MNHN): facultative, © Ifremer/A. Fifis)Six iconic animals from Alvin’s visits to seafloor vents
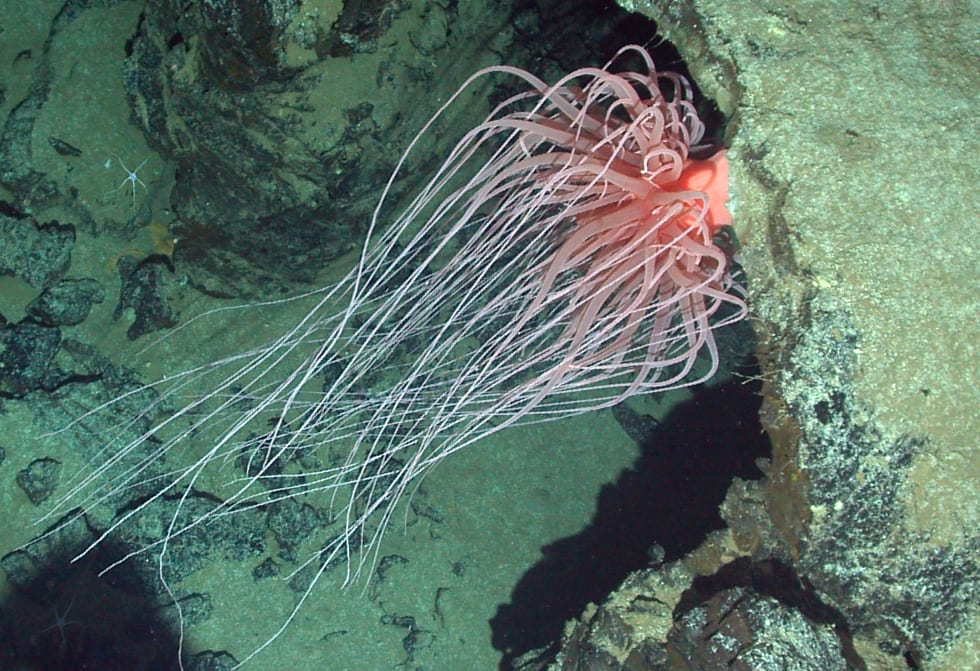
This creature (Relicanthus daphneae) was once thought to be the world’s largest sea anemone. It has tentacles more than six feet long. Alvin collected samples of it in 2003 on the East Pacific Rise. Results of genetic analysis, published May 9, 2014, show that this creature is in an entirely new order of animals, about as different from anemones as a dog is from a horse.
(© NOC/NERC)
Image and Visual Licensing
WHOI copyright digital assets (stills and video) contained on this website can be licensed for non-commercial use upon request and approval. Please contact WHOI Digital Assets at images@whoi.edu or (508) 289-2647.