Topic Page
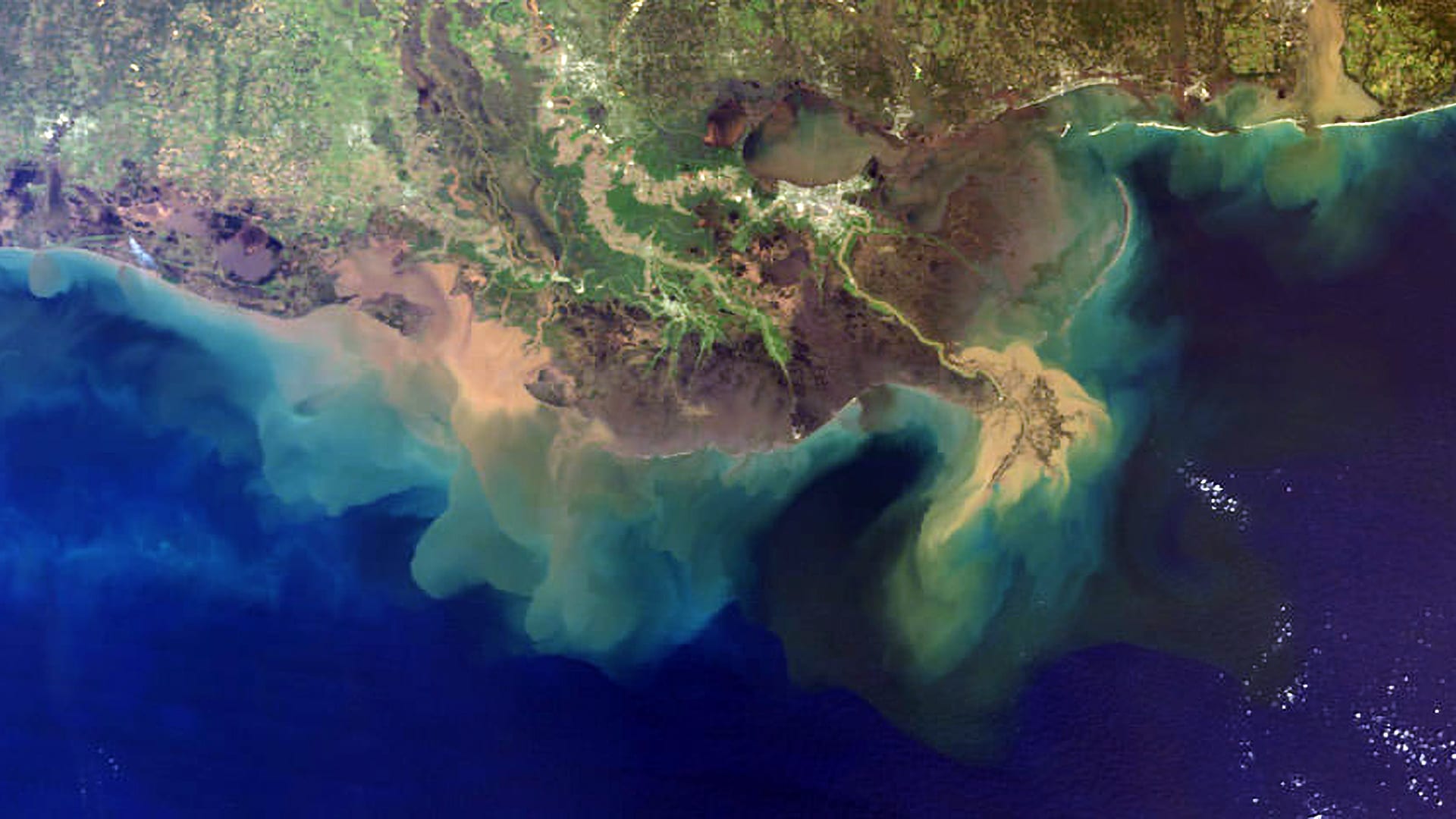
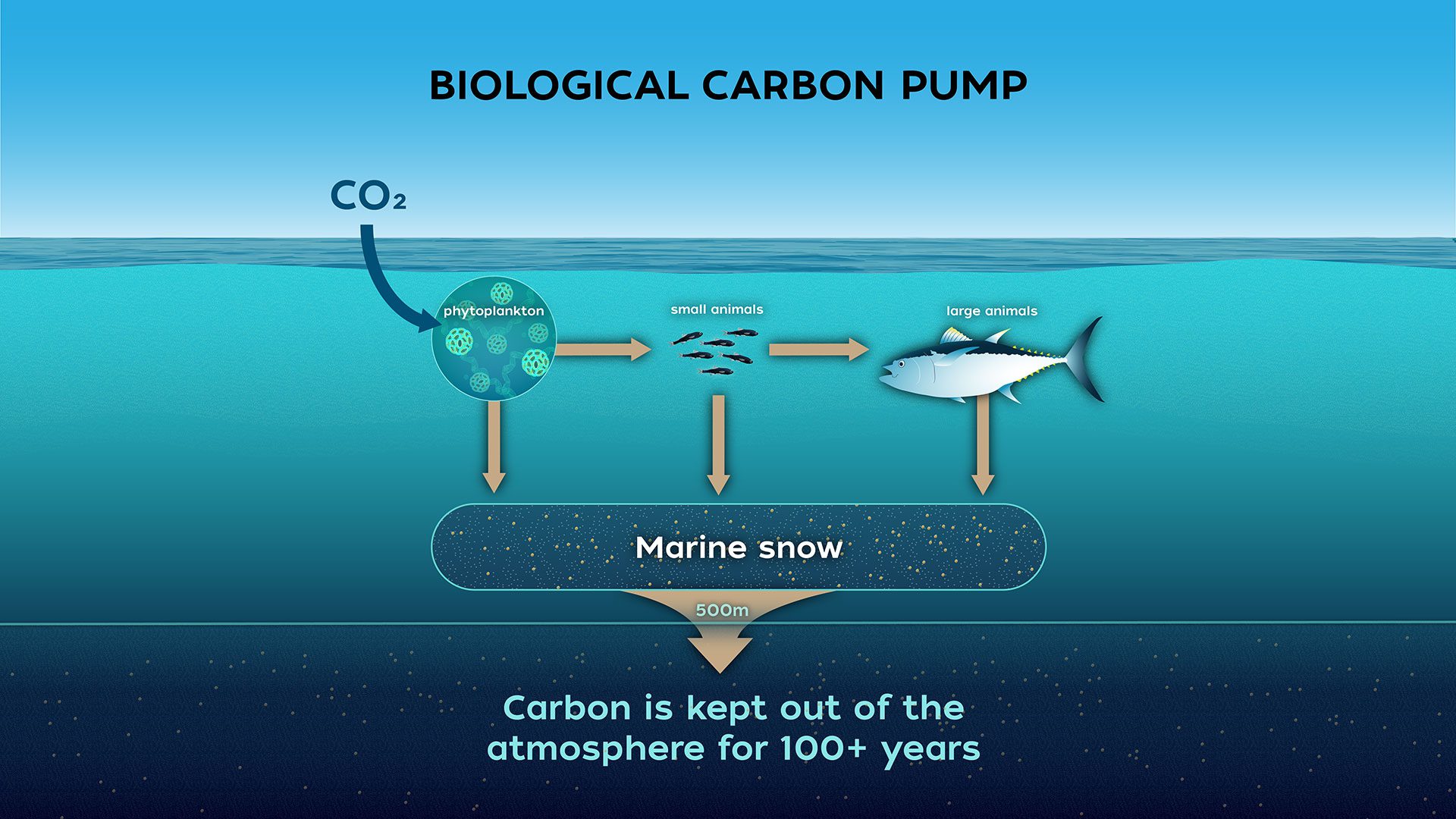
Biological Carbon Pump
The biological carbon pump removes atmospheric carbon by transporting carbon-rich material from surface waters to the deep ocean, aiding climate regulation.
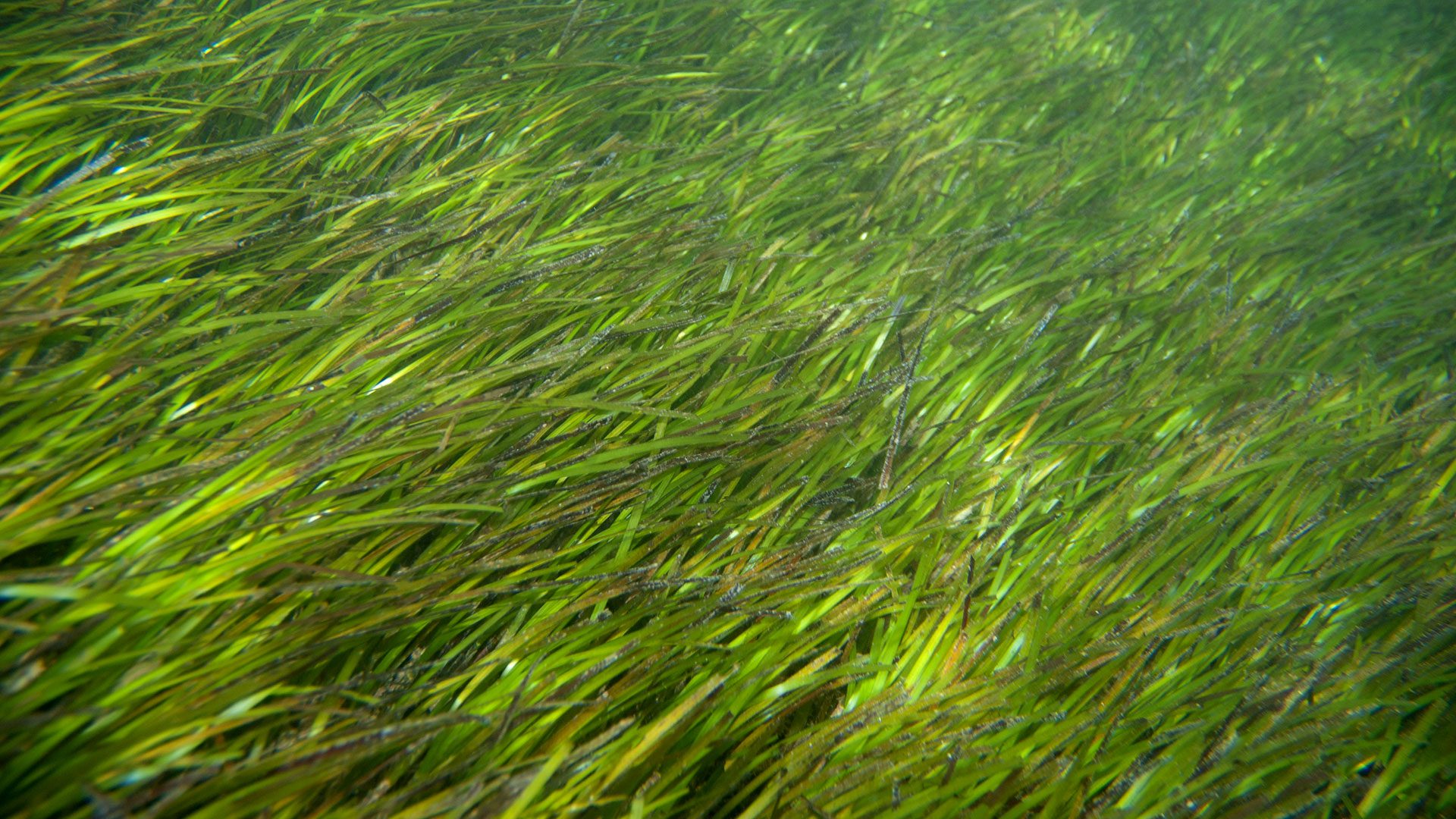
Read MoreSeagrass Meadows
Seagrass meadows are plants adapted to live a completely submerged life in the salty shallows.
Read MoreEnvironmental DNA (eDNA)
Environmental DNA (eDNA) is essentially DNA collected from the environment. As animals swim through the ocean, they’re constantly releasing DNA as they shed skin or scales into the water column.
Read MoreOxygen Dead Zones
Dead zones occur when the water lacks oxygen. Like us, marine animals require oxygen to breathe, and when oxygen levels drop too low they can suffocate.
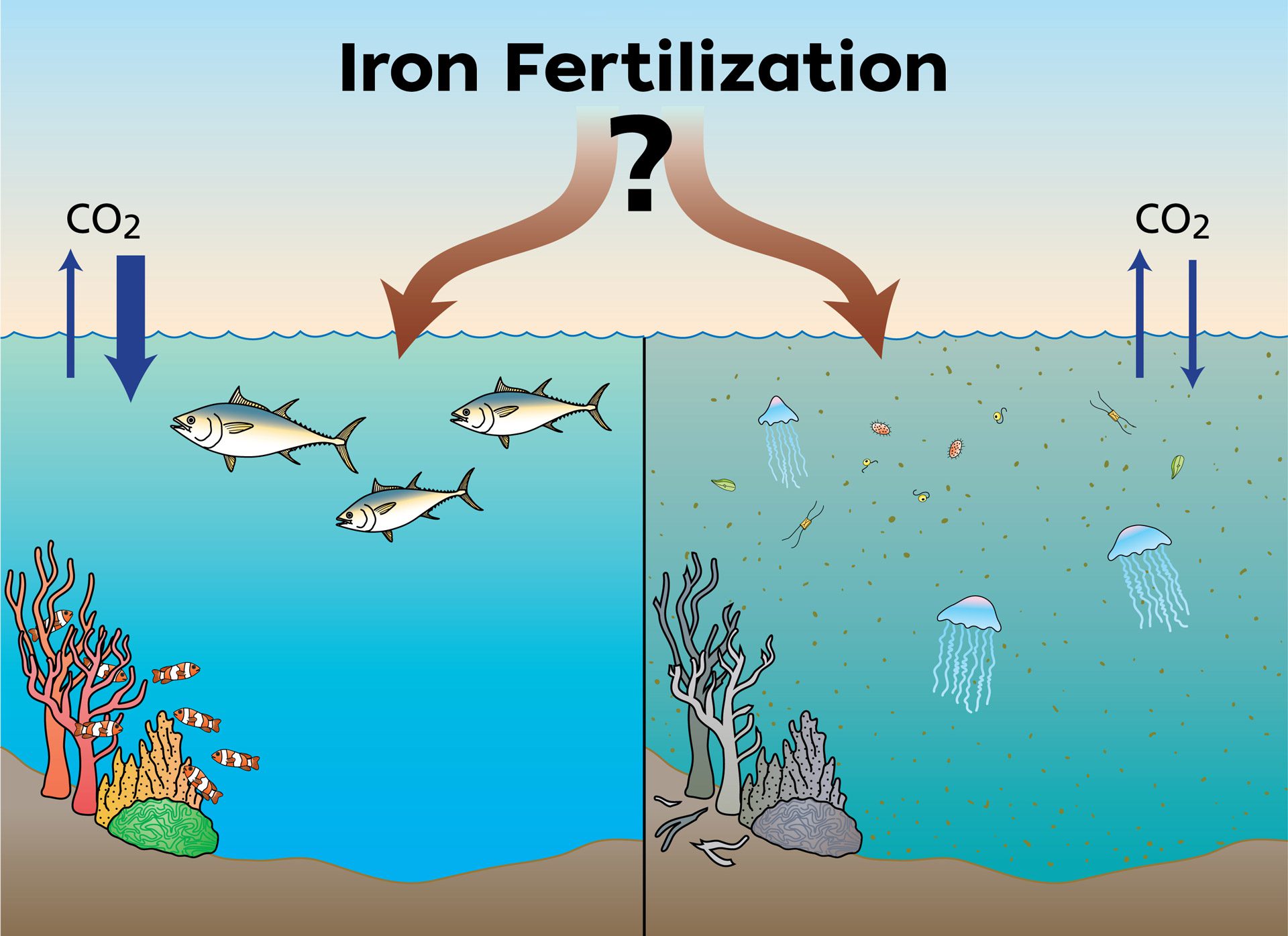
Read MoreIron Fertilization
Iron fertilization is a technique that would artificially add iron to the ocean’s surface, triggering massive blooms of phytoplankton that could remove substantial amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Read MoreOcean Modeling
Ocean models are mathematical models of ocean properties and circulation, which helps us to better understand the ocean’s influence on weather and climate.
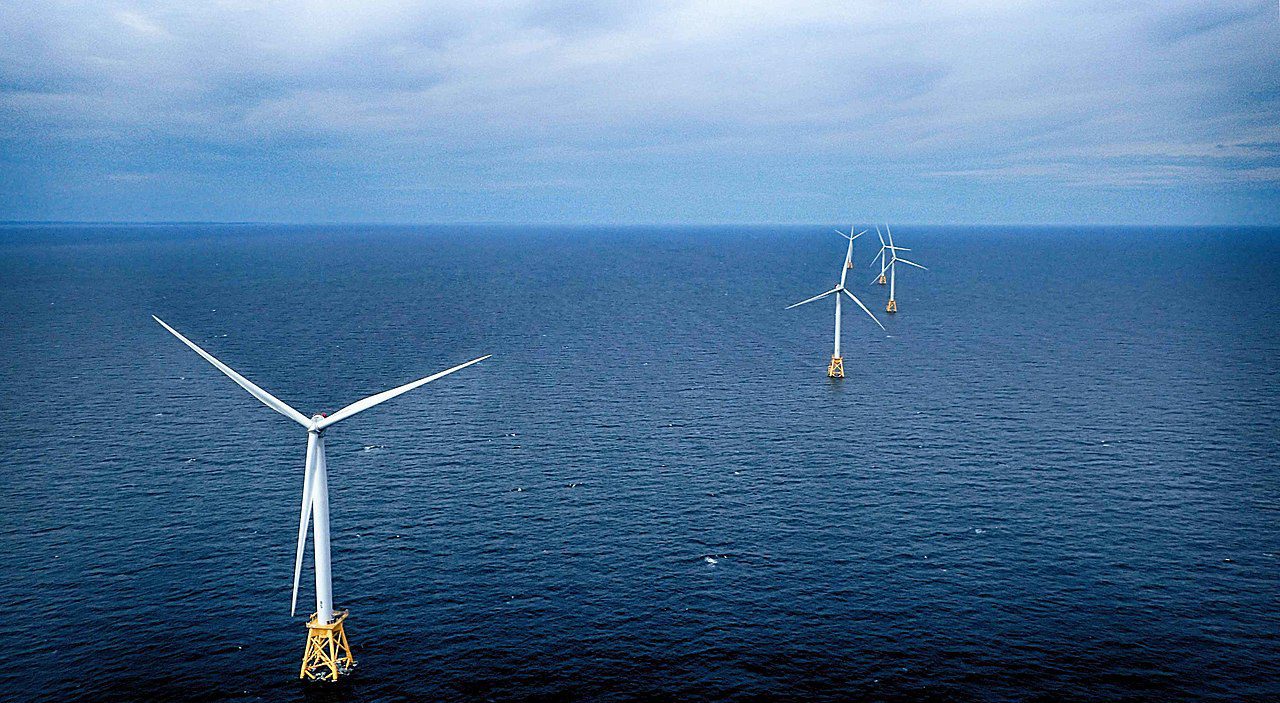
Read MoreOffshore Wind
Offshore wind energy generates electricity through wind farms along inshore water areas such as lakes, fjords and sheltered coastal areas, as well as deeper-water areas.
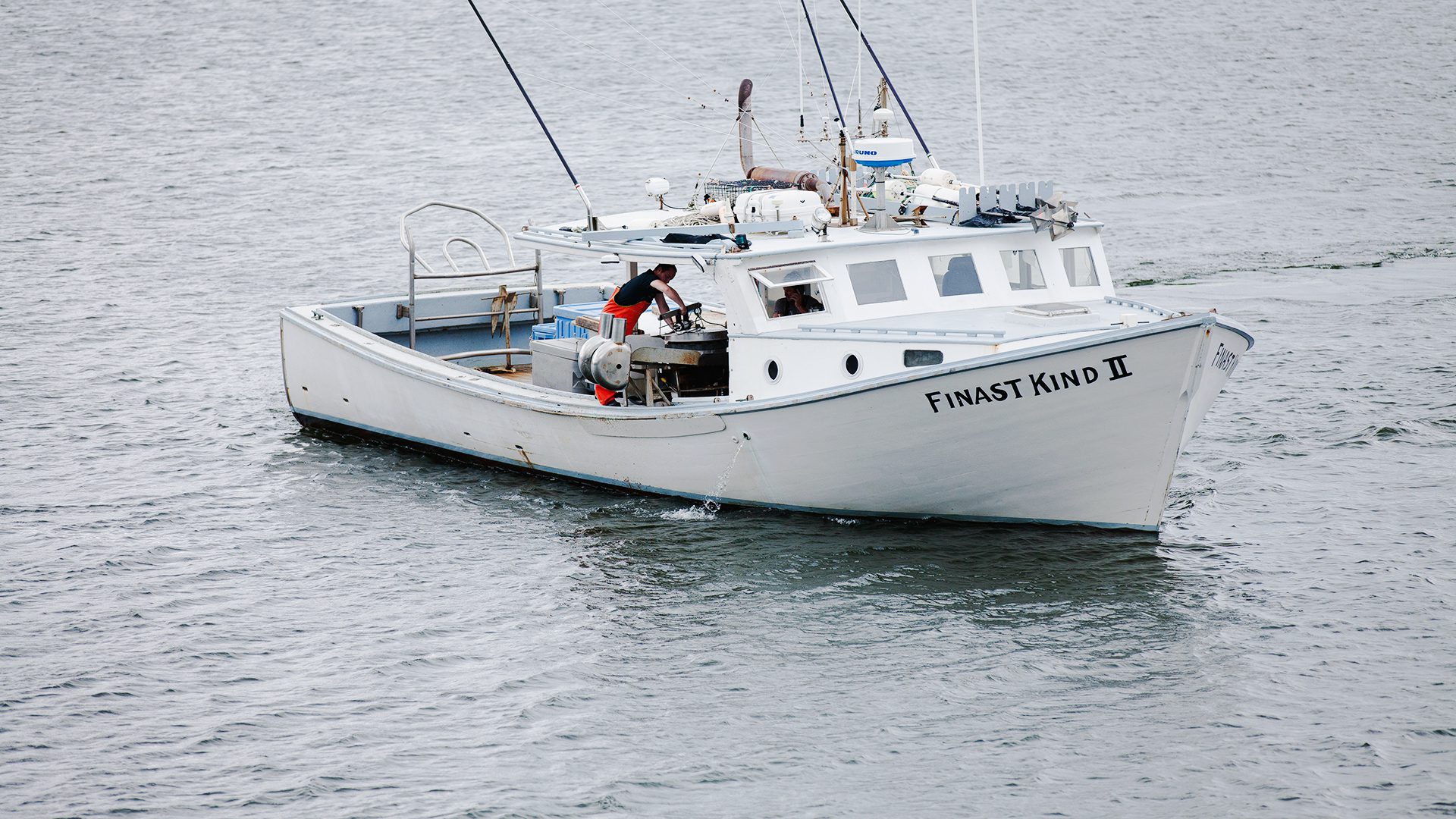
Read MoreFisheries
Overfishing and environmental issues have led to a decline in fish populations, creating uncertainty worldwide and threatening global economic and food security.
Read MoreSea Birds
Seabirds have adapted to life in an ocean environment. There are many species of seabirds, and they vary greatly in behavior and physiology
Read MoreAlgae
The term algae includes many different unicellular organisms capable of producing oxygen through photosynthesis, and are not necessarily closely related to each other.
Read MoreOcean Plants
Ocean plants are critical to marine life—they are an important food source, they provide oxygen to surrounding marine life, and they supply refuge and nursery grounds.
Read MoreBenthic Life
Benthic animals live on the sea floor and are typically invertebrates, such as sea anemones, sponges, corals, sea stars, sea urchins, worms, mussels, crabs, and more.
Read MoreReef Ecosystems
A healthy reef protects coastlines from wave damage, plays a critical role in providing food, boosts the economy, and provides materials for pharmaceuticals.
Read MoreStellwagen Bank
The shallow waters of the Stellwagen Bank create treacherous conditions that change unexpectedly and have led to numerous shipwrecks that dot the seafloor.
Read MoreStorms, Floods & Droughts
The source of the rain that filled your town reservoir, or flooded your nearby river, or never arrived to water your crops, is most likely the ocean.
Read MoreOcean Culture & History
The role of the ocean in human culture is profound, as people experience the sea in many ways, and respond with literature, art, and scientific investigation.
Read MoreRadiation
The background level of radiation in oceans and seas varies around the globe. Measured in atomic disintegrations per second (Becquerels) of cesium-137 in a cubic meter of water.
Read MoreOcean-Atmosphere Connection
The complex connections of these two systems are responsible for Earth’s weather and climate.
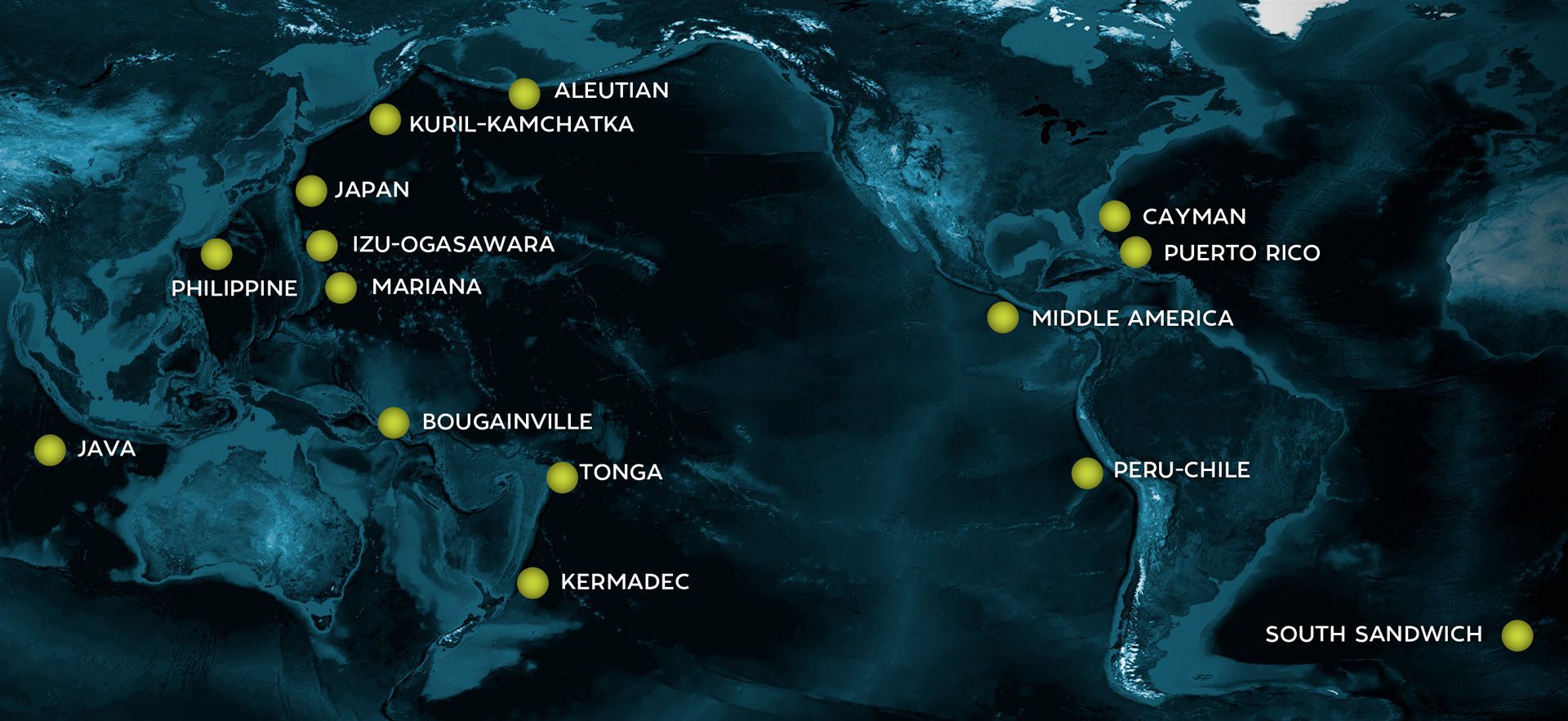
Read MoreHadal Zone
The region extending from 6,000 to 11,000 meters is called the hadal, or hadalpelagic, zone after Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. They occur only in trenches across the world.
Read MoreMidnight Zone
The midnight zone, or bathypelagic, extends to about 4,000 meters (about 13,100 feet), which reaches the ocean floor in many places is in perpetual darkness.
Read MoreSunlit Zone
The upper layer of the ocean is known as the sunlit, or euphotic, zone. Because water strongly absorbs light, sunlight penetrates only to depths of about 200 meters (656 feet).
Read MoreAbyssal Zone
The abyssal zone, or the abyss, is the seafloor and water column from 3,000 to 6,500 meters (9,842 to 21,325 feet) depth, where sunlight doesn’t penetrate.
Read MoreOcean Zones
The ocean water column is made up of five zones: the sunlight (epipelagic), twilight (mesopelagic), midnight (bathypelagic), abyssal (abyssopelagic) and hadal zones (trenches).
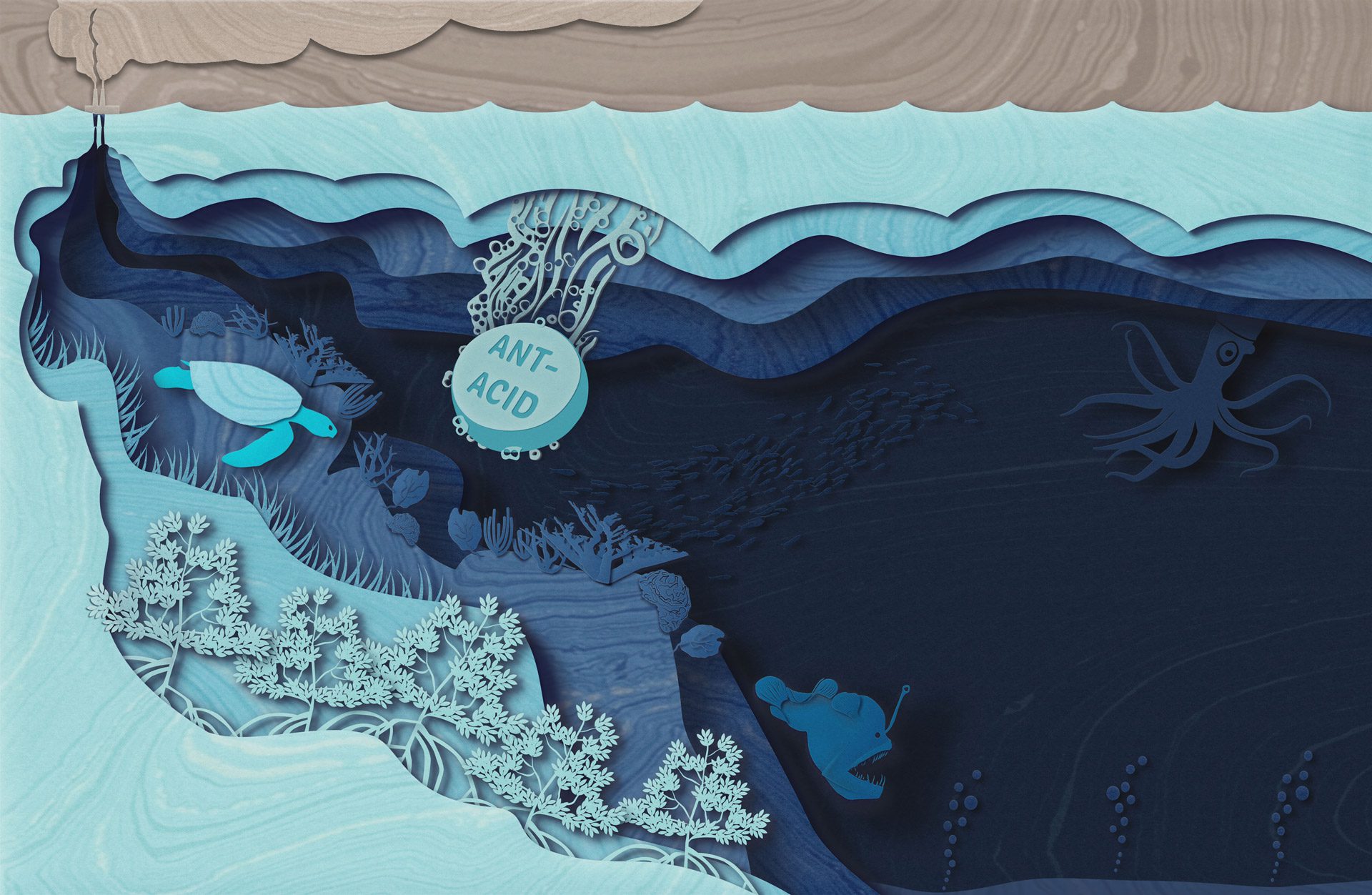
Read MoreOcean Alkalinity
When alkalinity reacts with carbon dioxide in the ocean, it converts it to a form that can’t readily return to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas.
Read More