News Releases
Ancient groundwater records reveal regional vulnerabilities to climate change
New WHOI-led study shows the Southwest may be more sensitive to drying than the Pacific Northwest
Read MoreResearchers Find Substantial Amount of Mercury Entering the Ocean through Groundwater
Researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have found a new and substantial pathway for mercury pollution flowing into coastal waters. Marine chemists have detected much more dissolved mercury entering the ocean through groundwater than from atmospheric and river sources.
Read MoreFreshwater and Saltwater Interactions in Coastal Groundwater Systems May Provide Clues to Chemicals Entering Coastal Waters
Scientists have recently recognized an imbalance in the flow of salty groundwater into the coastal ocean: considerable saltwater discharge into the ocean has been observed, but little or no return…
Read MorePaleoclimate data show land will warm more than sea
Understanding differences in land vs. sea temperatures may improve climate models, says WHOI study
Read MoreStudy Finds 6⁰C Cooling on Land during the Last Ice Age, With Implications about Future Global Warming
A recent report shows that prior studies have underestimated the cooling in the last glacial period, which has low-balled estimates of the Earth’s climate sensitivity to greenhouse gases. The rather high climate sensitivity is not good news regarding future global warming, which may be stronger than expected using previous best estimates.
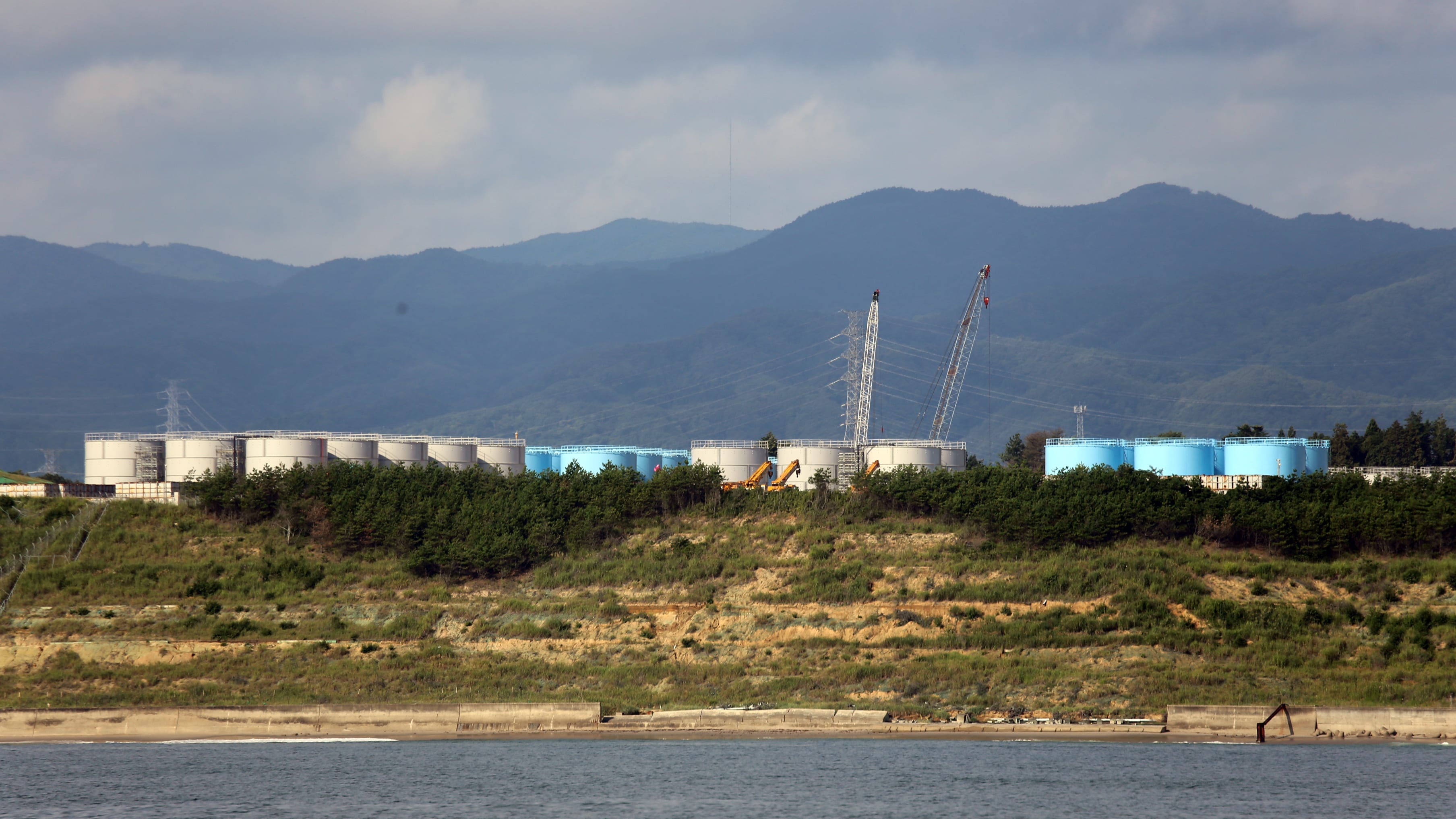
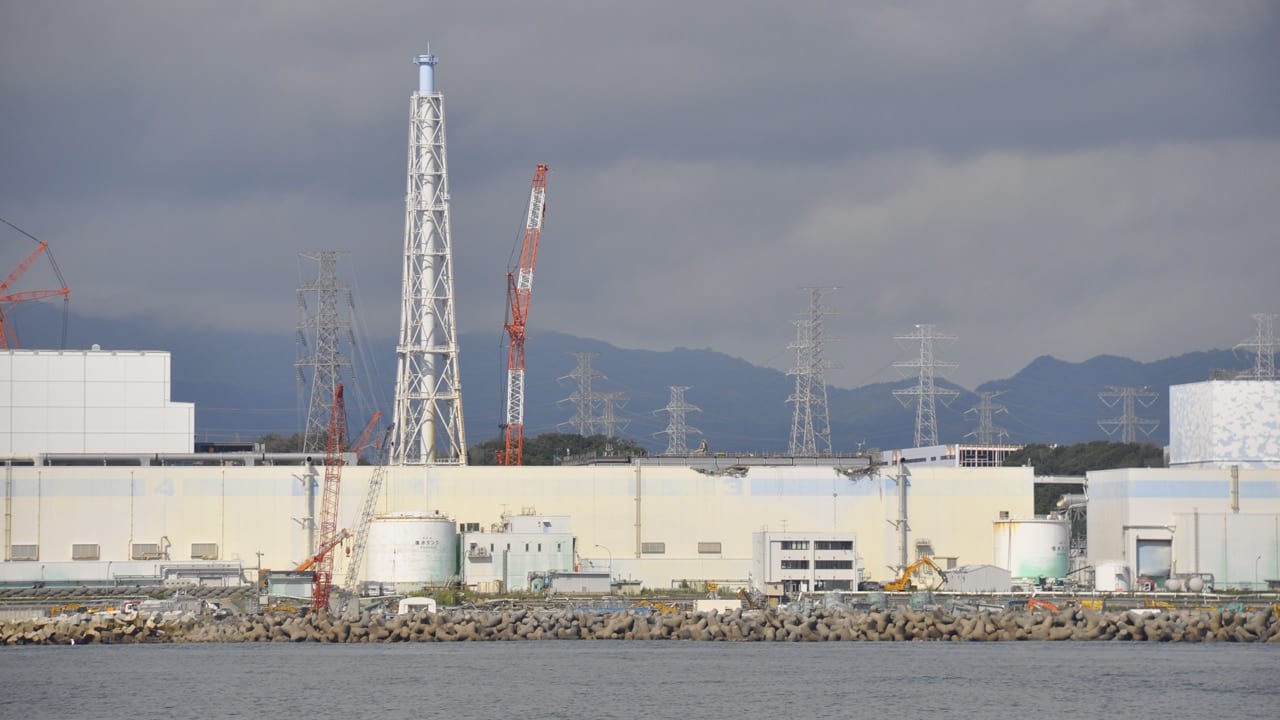
Read MoreNew paper addresses the mix of contaminants in Fukushima wastewater
A new study in the journal Science addresses recent suggestions that treated wastewater from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant should be dumped in the ocean.
Read MoreWhy Is Sea Level Rising Faster in Some Places Along the U.S. East Coast Than Others?
Sea levels are rising globally from ocean warming and melting of land ice, but the seas aren’t rising at the same rate everywhere. Sea levels have risen significantly higher in some U.S. East Coast regions compared to others. A new study led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) reveals why.
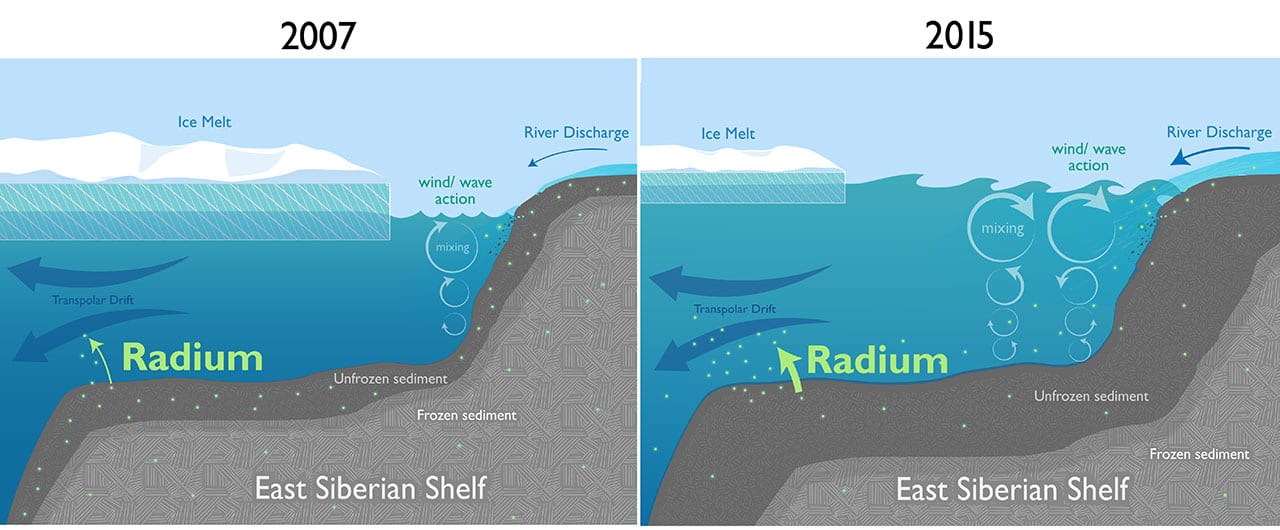
Read MoreScientists Find Surprising Evidence of Rapid Changes in the Arctic
Scientists have found surprising evidence of rapid climate change in the Arctic: In the middle of the Arctic Ocean near the North Pole, they discovered that the levels of radium-228 have almost doubled over the last decade.
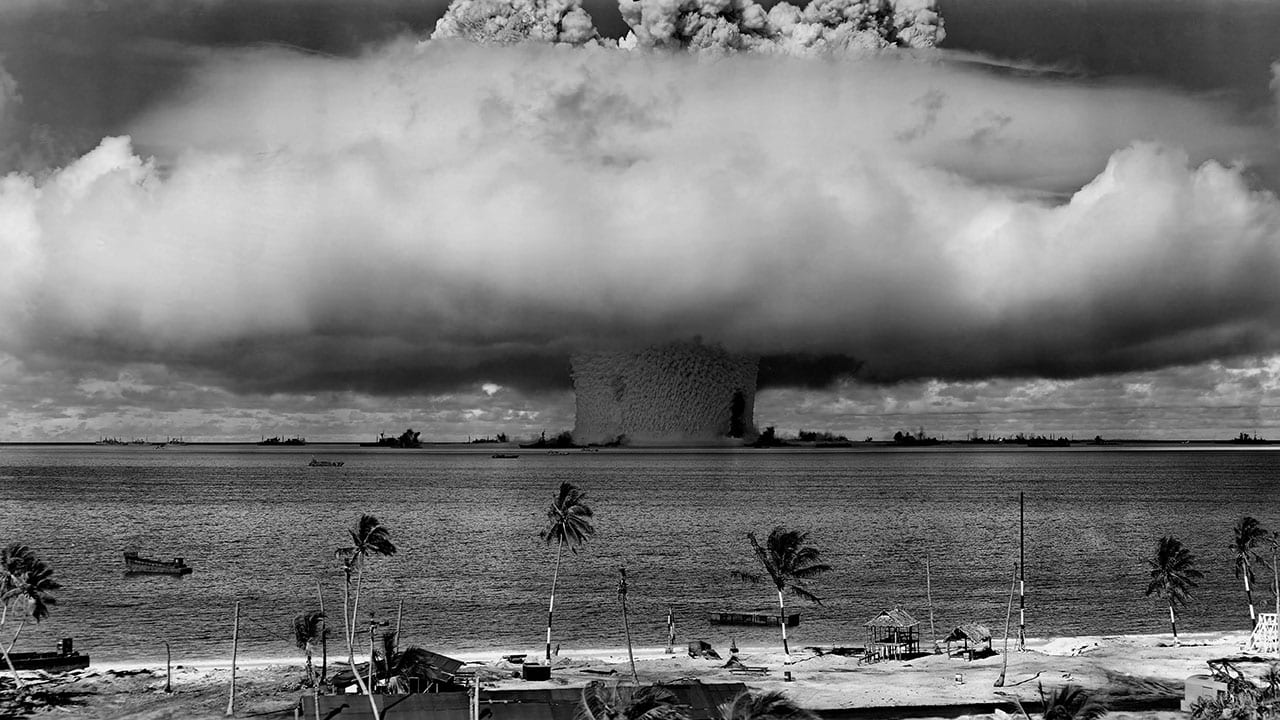
Read MoreRadioactivity Lingers from 1946-1958 Nuclear Bomb Tests
Scientists have found lingering radioactivity in the lagoons of remote Marshall Island atolls in the Pacific Ocean where the United States conducted 66 nuclear weapons tests in the 1940s and…
Read MoreScientists Find New Source of Radioactivity from Fukushima Disaster
Scientists have found a previously unsuspected place where radioactive material from the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant disaster has accumulated’in sands and brackish groundwater beneath beaches up to 60 miles away. The sands took up and retained radioactive cesium originating from the disaster in 2011 and have been slowly releasing it back to the ocean.
Read MoreFukushima Site Still Leaking After Five Years, Research Shows
Five years after the Fukushima accident, scientific data about the levels of radioactivity in the ocean off our shores are available publicly thanks to ongoing efforts of independent researchers, including WHOI radiochemist Ken Buesseler, who has led the effort to create and maintain an ocean monitoring network along the U.S. West Coast.
Read MoreHigher Levels of Fukushima Cesium Detected Offshore
Scientists monitoring the spread of radiation in the ocean from the Fukushima nuclear accident report finding an increased number of contaminated sites off the US West Coast, along with the highest detection level to date, from a sample collected about 1,600 miles west of San Francisco. The level of cesium in the sample is 50 percent higher than other samples collected, but is still more than 500 times lower than US government safety limits for drinking water and well below limits of concern for direct exposure while swimming, boating, or other recreational activities.
Ken Buesseler, a marine radiochemist with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and director of the WHOI Center for Marine and Environmental Radioactivity, was among the first to begin monitoring radiation in the Pacific, organizing a research expedition to the area just three months after the start of the ongoing accident. Through a citizen science sampling effort, Our Radioactive Ocean, as well as research funded by the National Science Foundation, Buesseler and his colleagues are using sophisticated sensors to measure minute levels of ocean-borne radioactivity from Fukushima. In 2015, they have added more than 50 new sample locations in the Pacific to the more than 200 previously collected and posted on the Our Radioactive Ocean web site.
Read MoreNew Research Shows Elevated Mercury from in-Ground Wastewater Disposal
As towns across Cape Cod struggle with problems stemming from septic systems, a recent study by a Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) scientist focuses on one specific toxic by-product: mercury.…
Read MoreResearchers Assess Radioactivity Released to the Ocean from the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Facility
The impact on the ocean of releases of radioactivity from the Fukushima nuclear power plants remains unclear. But a new study by U.S. and Japanese researchers analyzes the levels of radioactivity discharged from the facility in the first four months after the accident and draws some basic conclusions about the history of contaminant releases to the ocean.
Read MoreNauset Marsh Estuary Red Tide Study to Begin
A three-year study into the cause of local area red tides is set to begin March 21. A team of researchers from the National Park Service, U.S. Geological Survey, and…
Read MoreUndersea Cracks along Continental Shelf Could Trigger Tsunamis along U.S. East Coast
Potential landslides on the outer continental shelf and slope along the Mid-Atlantic coast could trigger tsunamis that might have devastating effects on populated coastal areas. In a paper published in the May 2000 issue of the journal Geology,Neal Driscoll of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and colleagues Jeffrey Weissel of Columbia University??A?s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory and John Goff of the University of Texas at Austin say newly discovered cracks along the edge of the continental shelf could be an early warning sign that the seafloor is unstable in these areas.
New Iron-Eating Microbe Major Component of Mining Pollution and Iron and Sulfur Cycling
A new microbe that eats iron and lives in some of the most acidic conditions found on earth has been identified as a major player in the environmental damage caused by metal ore mining. It also raises questions about the ability of microbes to survive in extremely toxic environments on earth or on other planets, and what role these organisms play in the cycling of iron and sulfur in the environment.
Read More