News Releases
New Technique Offers Clues to Measure Ocean Deoxygenation
The living, breathing ocean may be slowly starting to suffocate. More than two percent of the ocean – s oxygen content has been depleted during the last half century, according to reports, and marine – dead zones – continue to expand throughout the global ocean. This deoxygenation, triggered mainly by more fertilizers and wastewater flowing into the ocean, pose a serious threat to marine life and ecosystems.
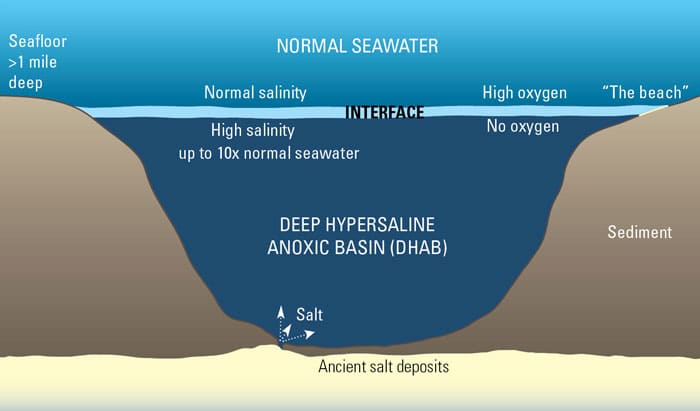
Read MoreCan animals thrive without oxygen?
In 2010, a research team garnered attention when it published evidence of finding the first animals living in permanently anoxic conditions at the bottom of the sea. But a new […]
Read MoreHuman-Engineered Changes on Mississippi River Increased Extreme Floods
Over the last century, many of the world’s major rivers have been modified for the purposes of flood control, power generation, and commercial navigation. A new study out of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution suggests that engineering modifications to the Mississippi River interact with the have increased the risk of extreme floods to unprecedented levels.
Read MoreDeep Biosphere Harbors Active, Growing Communities of Microorganisms
The deep biosphere—the realm of sediments far below the seafloor—harbors a vast ecosystem of bacteria, archaea, and fungi that are actively metabolizing, proliferating, and moving, according a new study by […]
Read MoreWHOI Scientists Map and Confirm Origin of Large, Underwater Hydrocarbon Plume in Gulf
Scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) detected and characterized a plume of hydrocarbons that is at least 22 miles long and more than 3,000 feet below the surface of the Gulf of Mexico, a residue of the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill. The work presents a forensic snapshot of the plume characteristics in June and is reported in a study appearing in the Aug. 19 issue of the journal Science.
Read MoreAcid Rain Has a Disproportionate Impact on Coastal Waters
The release of sulfur and nitrogen into the atmosphere by power plants and agricultural activities plays a minor role in making the ocean slightly more acidic on a global scale, but the impact is greatly amplified in the shallower waters of the coastal ocean, according to new research by atmospheric and marine chemists.
Read More