News Releases
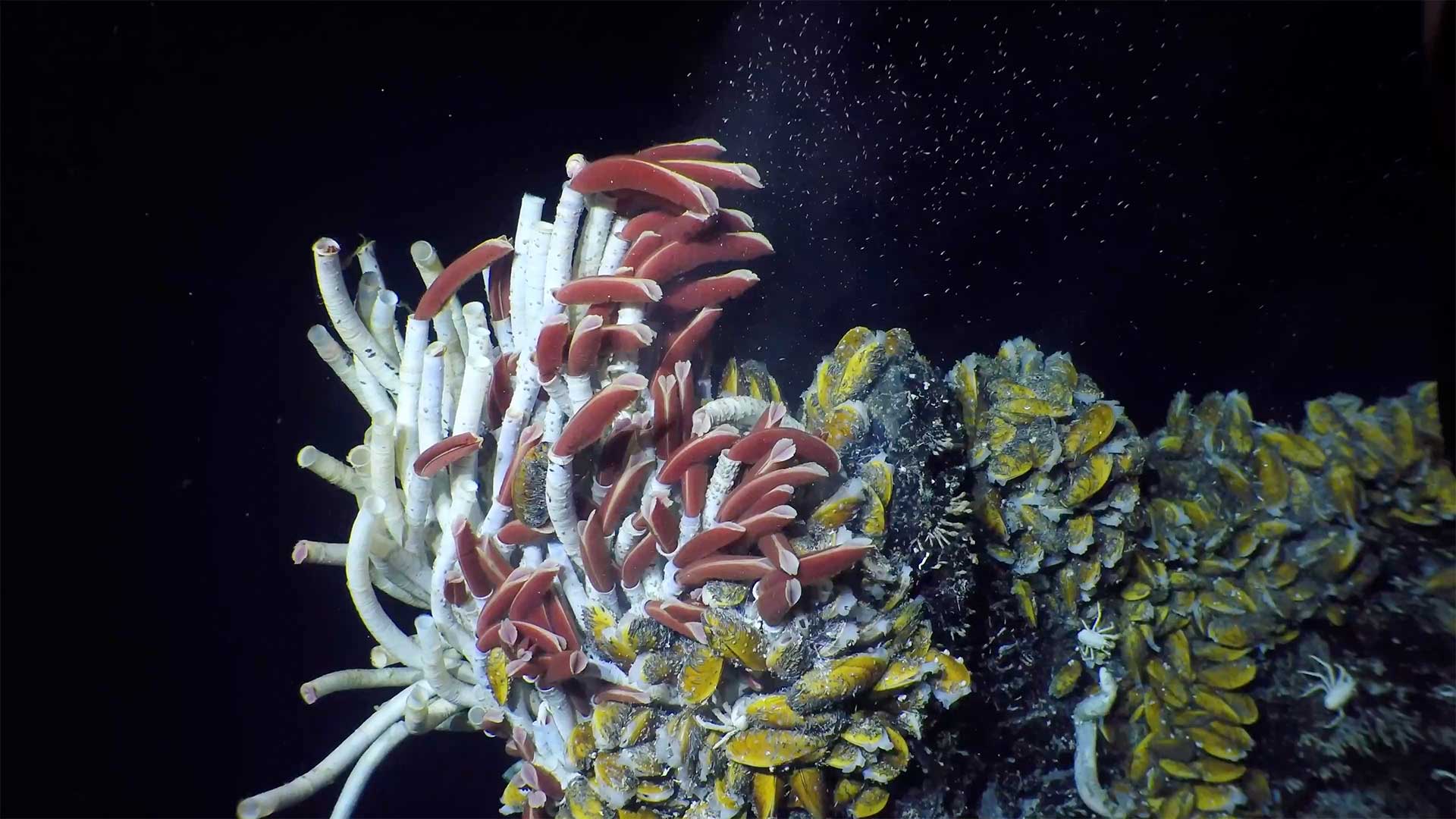
Study weighs deep-sea mining’s impact on microbes
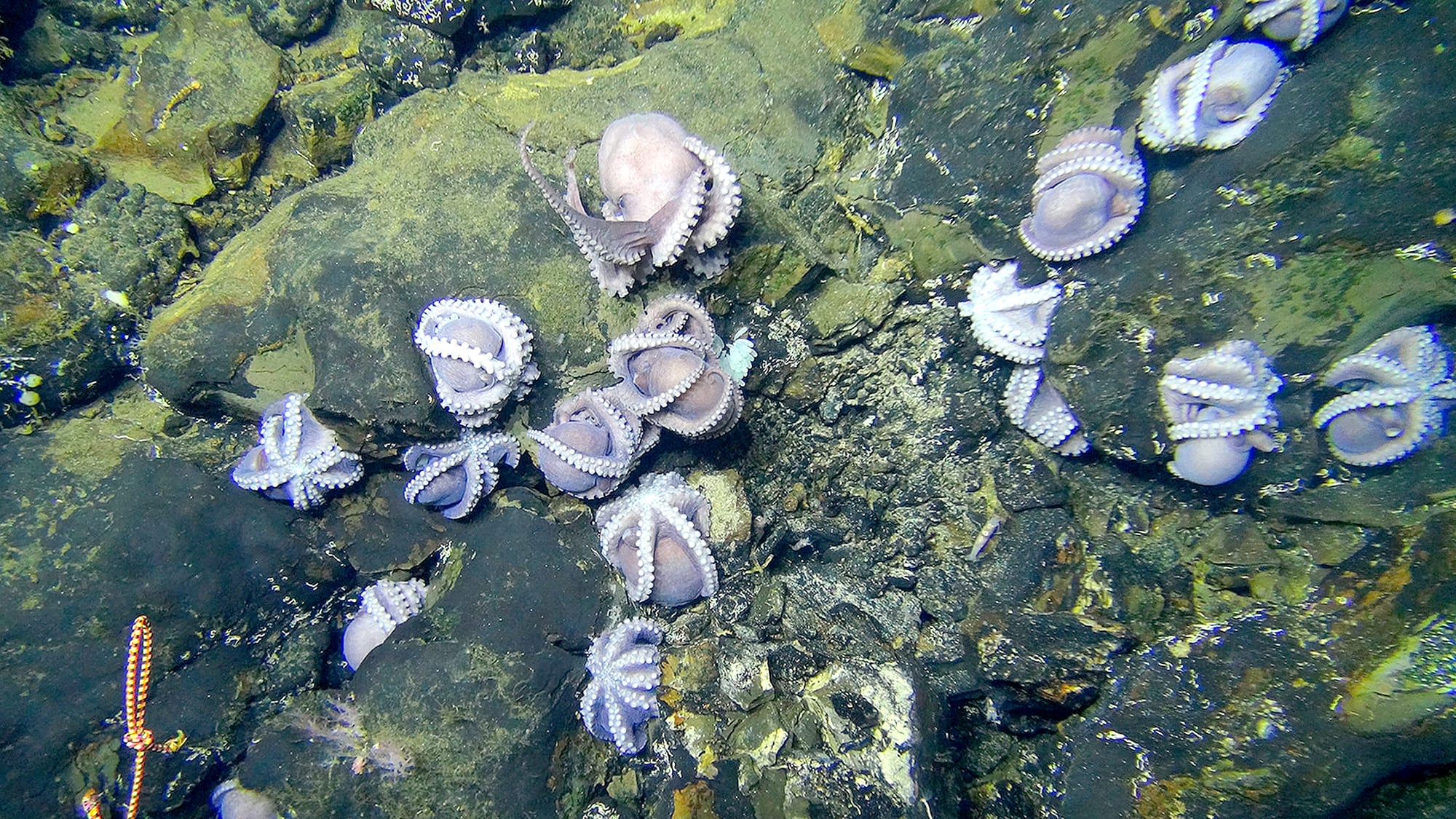
The essential roles that microbes play in deep-sea ecosystems are at risk from the potential environmental impacts of mining, according to a new paper. The study reviews what is known about microbes in these environments and assesses how mining could impact their important environmental roles.
Read MorePanel to Discuss Deep-Sea Mining at AAAS Meeting
Home to an immense diversity of marine life, the deep ocean also contains valuable minerals with metals such as nickel, copper, cobalt, manganese, zinc, and gold, and rare-earth elements used in electronic technology like smart phones and medical imaging machines. As demand for these resources increases and supplies on land decrease, commercial mining operators are looking to the deep ocean as the next frontier for mining.
Read MoreExamining the Fate of Fukushima Contaminants
An international research team reports results of a three-year study of sediment samples collected offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in a new paper published August 18, 2015, in the American Chemical Society’s journal, Environmental Science and Technology. The research aids in understanding what happens to Fukushima contaminants after they are buried on the seafloor off coastal Japan.
Read MoreDeep Sea Floor Mining Is Subject of International Colloquium at WHOI
Scientists, policymakers, environmentalists, and industry representatives will gather next week at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) to discuss the issue of mining precious metals from the seafloor. A public colloquium, […]
Read MoreIn Computer Models and Seafloor Observations, Researchers See Potential for Significant 2008 “Red Tide” Season
Researchers from WHOI and North Carolina State University are preparing for a potentially big bloom of harmful algae in New England waters this spring. A combination of abundant beds of algal seeds and excess winter precipitation have set the stage for an Alexandrium bloom similar to the historic “red tide” of 2005. Weather patterns and ocean conditions over the next few months will determine whether this year’s algal growth affects coastal shellfishing.
Read MoreFragmented Structure of Seafloor Faults May Dampen Effects of Earthquakes
Many earthquakes in the deep ocean are much lower in magnitude than expected. Geophysicists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have found new evidence that the fragmented structure of seafloor faults and previously unrecognized volcanism may be dampening the effects of these quakes.
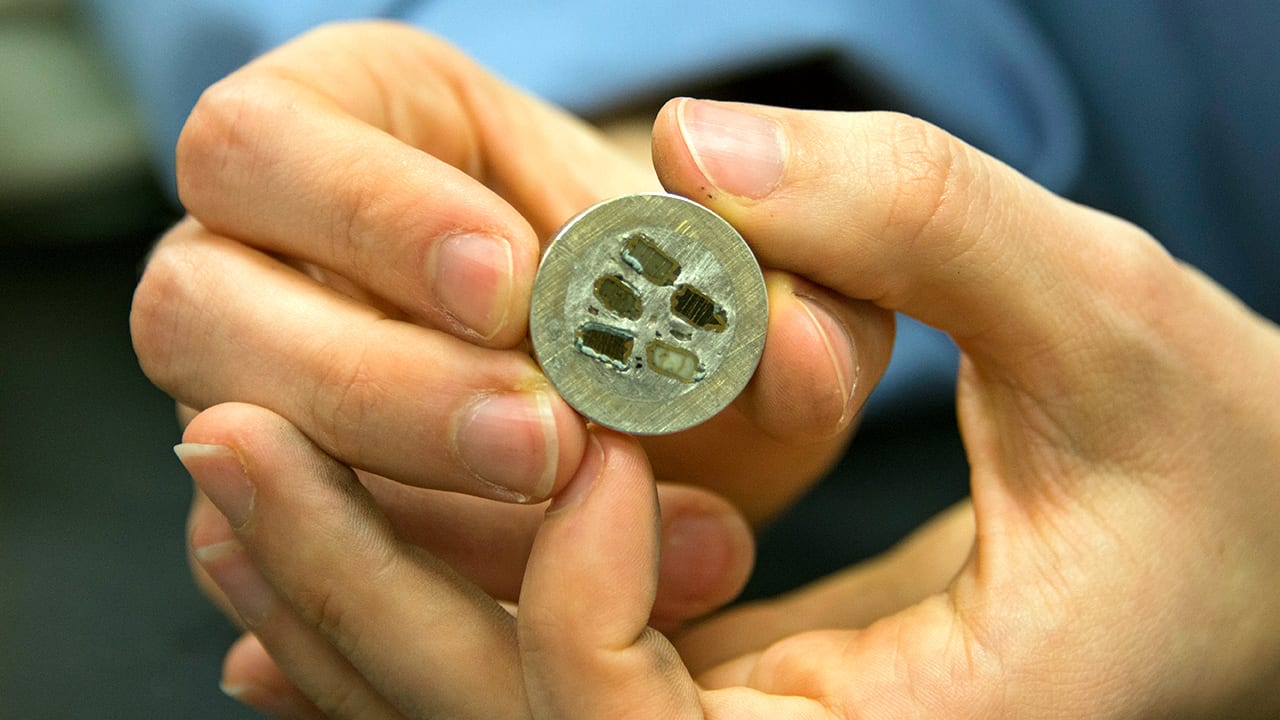
Read MoreNew Iron-Eating Microbe Major Component of Mining Pollution and Iron and Sulfur Cycling
A new microbe that eats iron and lives in some of the most acidic conditions found on earth has been identified as a major player in the environmental damage caused by metal ore mining. It also raises questions about the ability of microbes to survive in extremely toxic environments on earth or on other planets, and what role these organisms play in the cycling of iron and sulfur in the environment.
Read MoreWarm water could persist within icy ocean worlds
A new study investigates how the influence of low gravity, as found on ocean worlds in our solar system, impacts flow of water and heat below their seafloors.
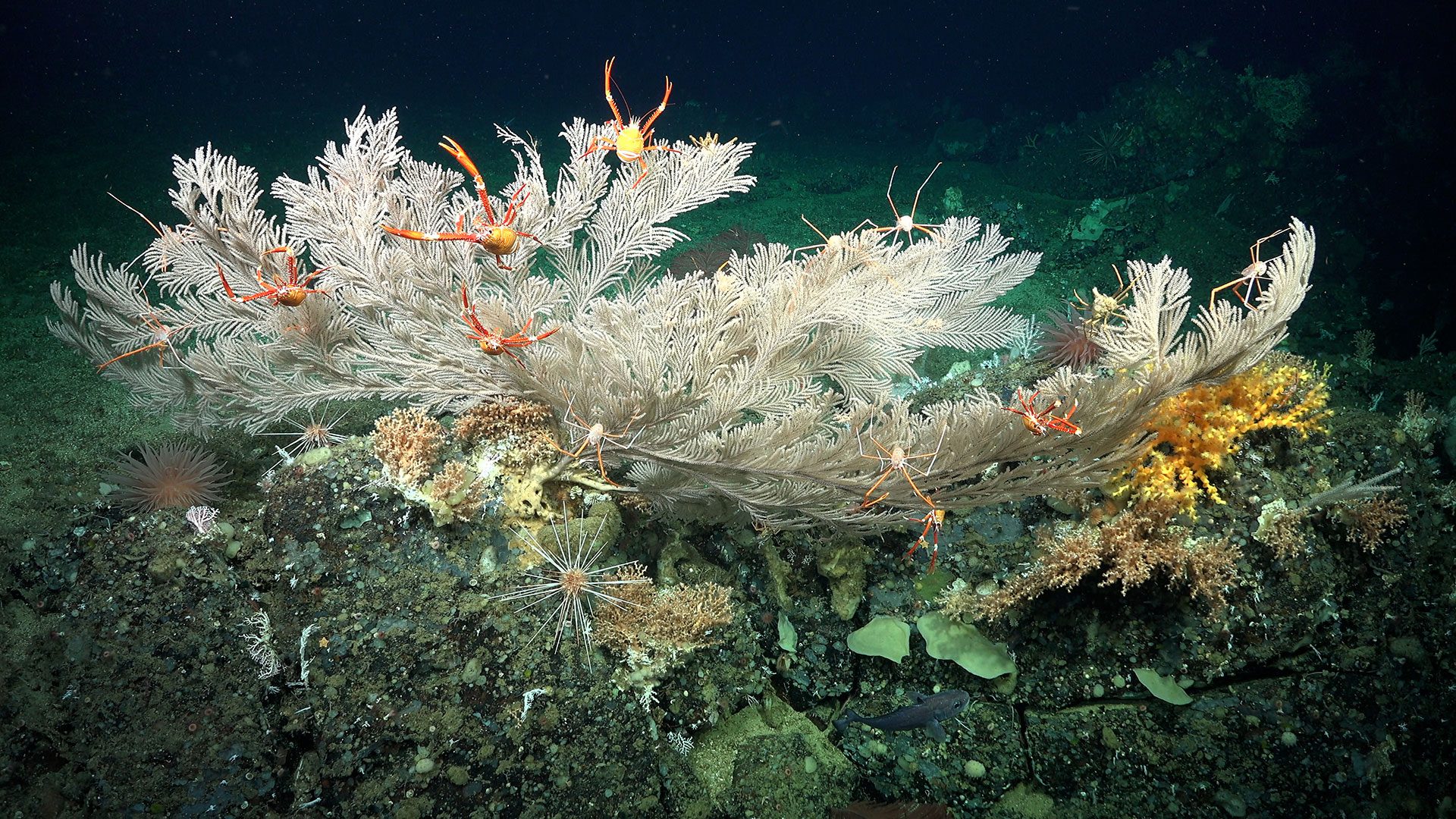
Read MoreScientists Discover Additional Healthy Deep-sea Coral Reefs and New Seamounts in the Galápagos
Stunning 800 meter-long coral reef discovered with Schmidt Ocean Institute’s underwater robot off Galápagos Islands
Puerto Ayora, Ecuador– Scientists examining underwater cliff ecosystems onboard research vessel Falkor(too) using the 4,500 meter […]
Read MoreArctic Hydrothermal Vent Site Could Help in Search for Extraterrestrial Life
When scientists discovered a hydrothermal vent site in the Arctic Ocean’s Aurora hydrothermal system in 2014, they did not immediately realize just how exciting their discovery was.
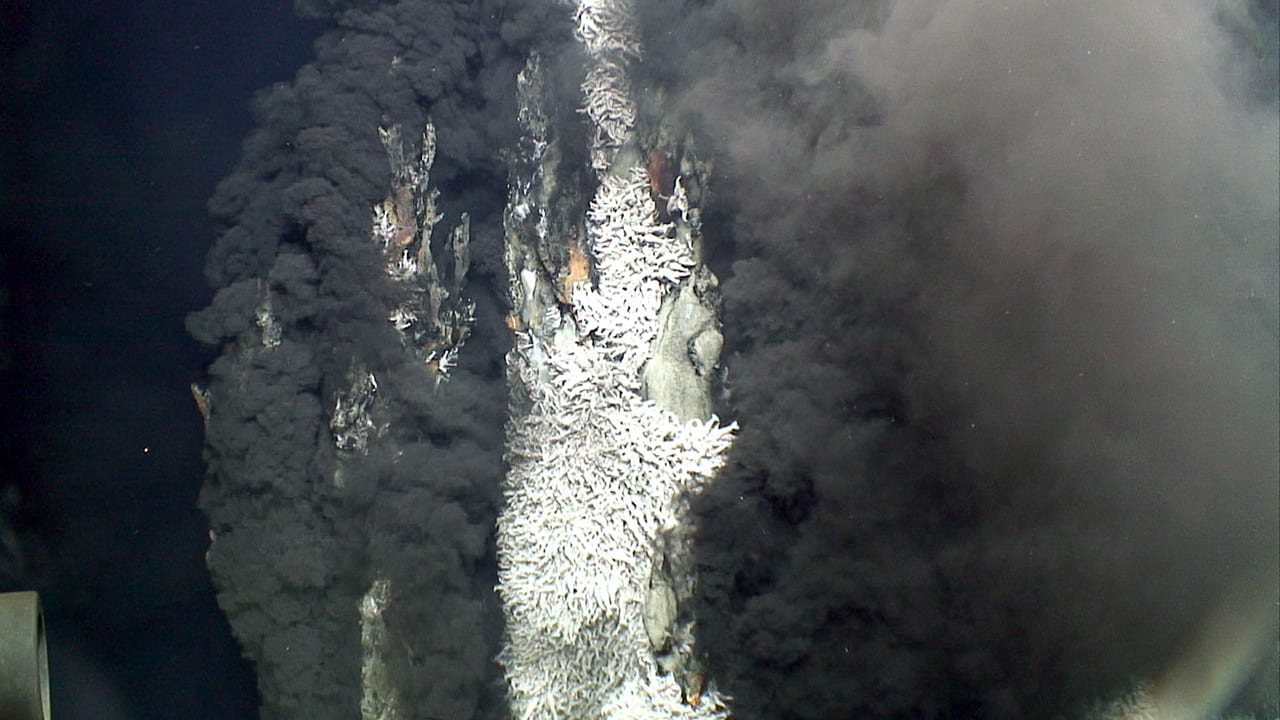
Read MoreFluid Flow Stimulates Chemosynthesis in a Greek Salad of Hydrothermal Microbes
A new study uses an innovative approach to examine the bay’s shallow-water hydrothermal system and the production of microbes there in situ and near natural conditions as a model to assess the importance of hydrothermal fluid circulation on chemosynthesis.
Read MoreScientists call for decade of concerted effort to improve understanding of the deep ocean
The deep ocean—vast expanses of water and seafloor more than 200 meters (660 feet) below the surface—are globally recognized as an important frontier of exploration and research.
Despite the fact they […]
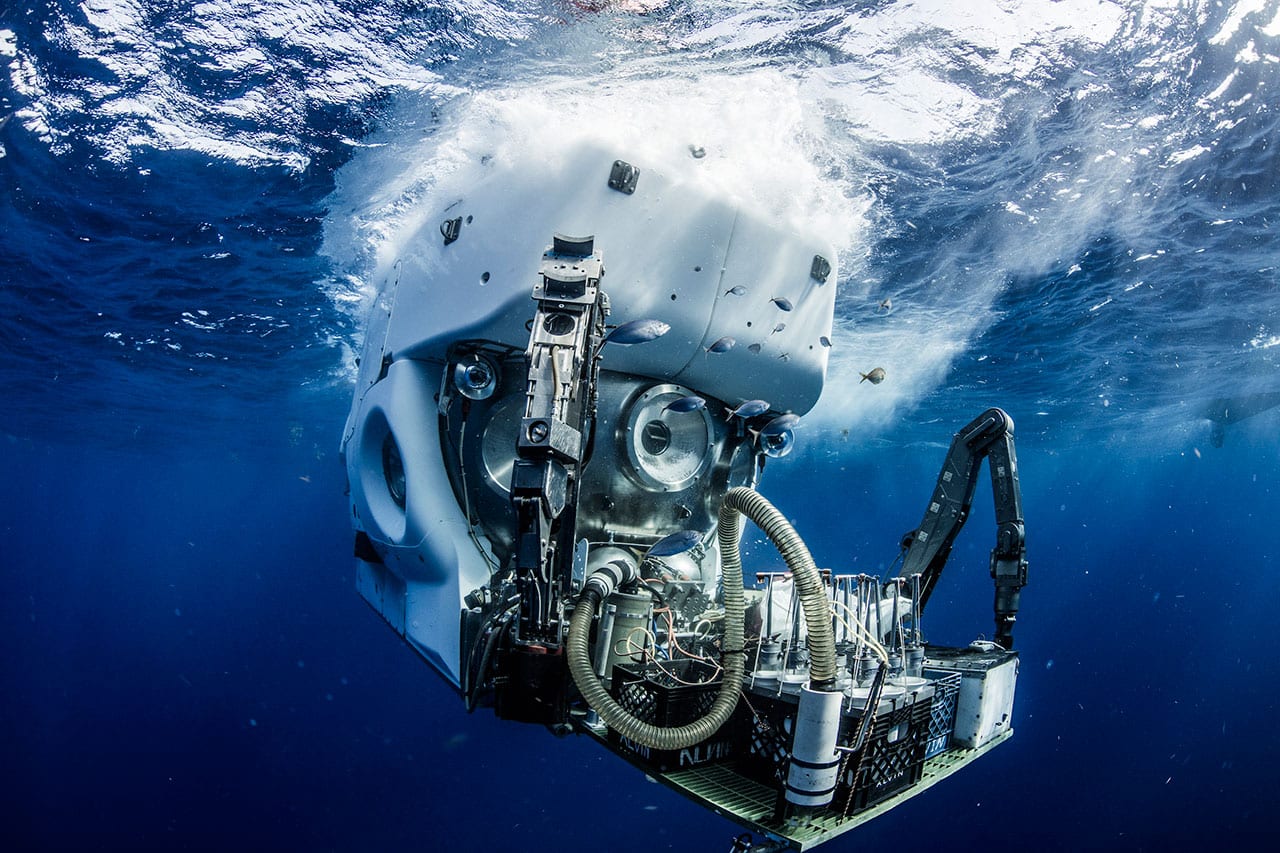
Read MoreAlvin Submersible Makes 5,000th Dive
Alvin, the country’s only deep-diving research submersible capable of carrying humans to the sea floor, reached another milestone in its long career on Nov. 26, 2018, when the sub made its 5,000th dive during an expedition to the Guaymas Basin in the Gulf of California.
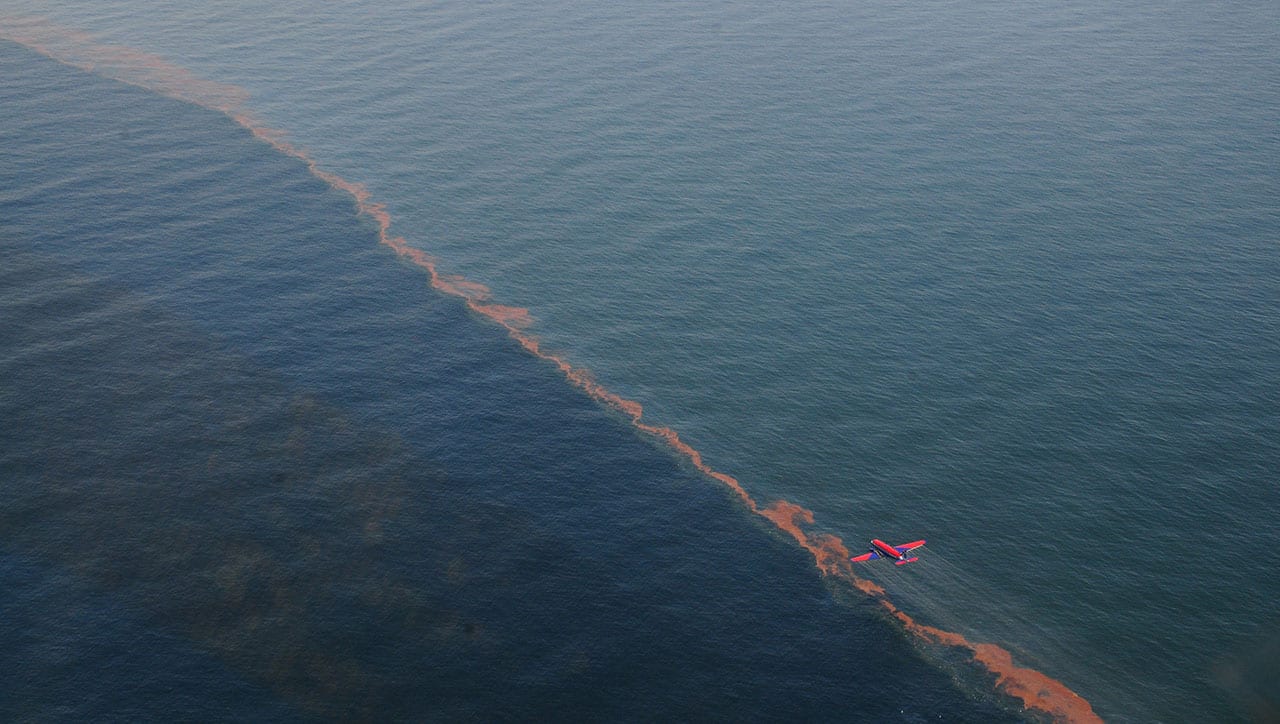
Read MoreSunlight Reduces Effectiveness of Dispersants Used in Oil Spills
A research team led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) found that sunlight chemically alters crude oil floating on the sea surface within hours or days. In a follow-up study the team reported that sunlight changes oil into different compounds that dispersants cannot easily break up. The results of these two studies could affect how responders decide when, where, and how to use dispersants.
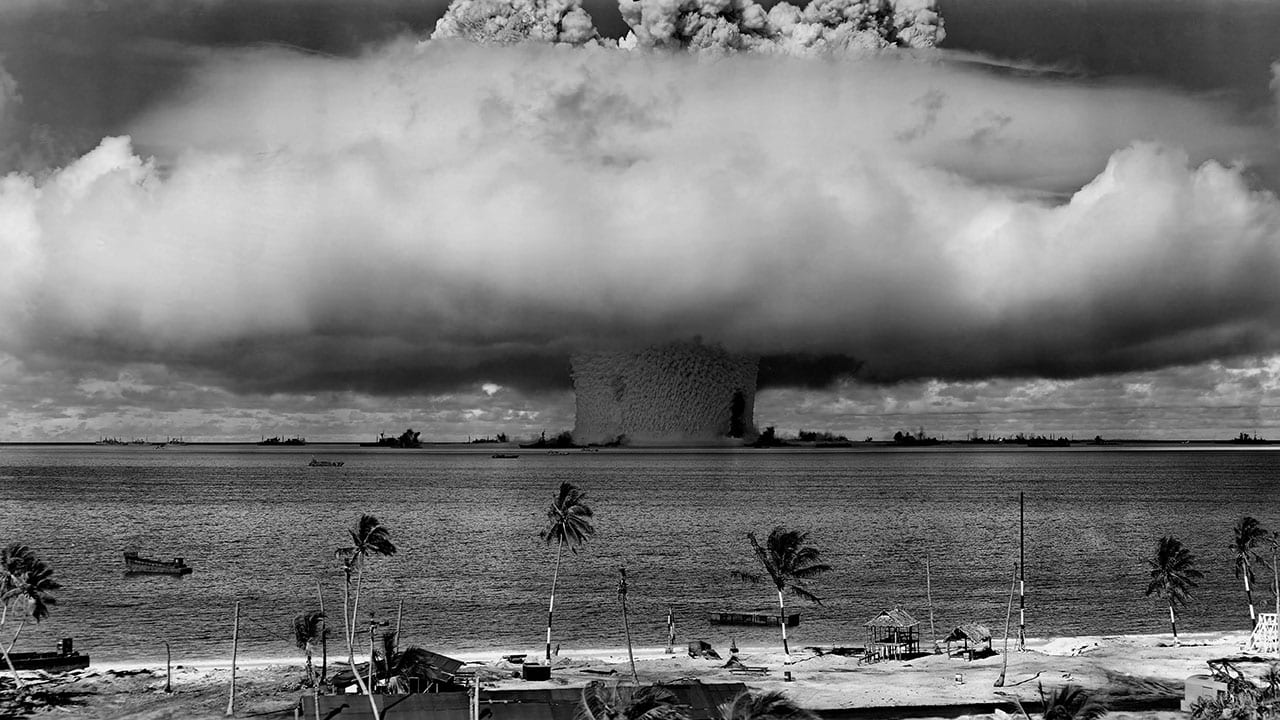
Read MoreRadioactivity Lingers from 1946-1958 Nuclear Bomb Tests
Scientists have found lingering radioactivity in the lagoons of remote Marshall Island atolls in the Pacific Ocean where the United States conducted 66 nuclear weapons tests in the 1940s and […]
Read MoreTaking Earth’s Inner Temperature
A new WHOI study led by WHOI suggests the mantleâÃÂÃÂthe mostly solid, rocky part of Earth’s interior that lies between its super-heated core and its outer crustal layerâÃÂÃÂmay be hotter than previously believed. The surprising finding could change how scientists think about many issues in Earth science including how ocean basins form.
Read MoreStudy Finds Deep Ocean is Source of Dissolved Iron in Central Pacific
A new study led by scientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) points to the deep ocean as a major source of dissolved iron in the central Pacific Ocean. This finding highlights the vital role ocean mixing plays in determining whether deep sources of iron reach the surface-dwelling life that need it to survive.
Read MoreScientific Mission Will Explore One of the Deepest Ocean Trenches
An international team of researchers led by deep-sea biologist Tim Shank of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) will use the world’s only full-ocean depth, hybrid remotely operated vehicle, Nereus, and other advanced technology to explore life in the depths of the Kermadec Trench.
Read MoreDeep-Diving Sub Alvin Cleared to Return to Service
After a three-year overhaul and major upgrade, the United States’ deepest-diving research submersible, Alvin, has been cleared to return to work exploring the ocean’s depths.
Read MoreSampling the Pacific for Signs of Fukushima
An international research team is reporting the results of a research cruise they organized to study the amount, spread, and impacts of radiation released into the ocean from the tsunami-crippled […]
Read MoreWHOI Researchers, Collaborators Receive $1.4 Million to Study Life in Ocean’s Greatest Depths
Scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), University of Hawaii, Whitman College and international colleagues will conduct the first systematic study of life in the deepest marine habitat on […]
Read MoreLong-Distance Larvae Speed to New Undersea Vent Homes
Working in a rare, ?natural seafloor laboratory? of hydrothermal vents that had just been rocked by a volcanic eruption, scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and other institutions have discovered what they believe is an undersea superhighway carrying tiny life forms unprecedented distances to inhabit the post-eruption site.
Read MoreNow in Broadband: Acoustic Imaging of the Ocean
Researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have developed two advanced broadband acoustic systems that they believe could represent the acoustic equivalent of the leap from black-and-white television to high-definition […]
Read MoreWHOI contributes to special seamount issue of Oceanography magazine
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) biologist Timothy M. Shank is among five guest editors of a newly published special edition of the research journal Oceanography on the oceans? seamounts, submerged isolated mountains in the sea. Shank is also a contributor to the special Oceanography edition.
Read More