News Releases
Galapagos Expedition Reveals Unknown Seamounts, New Species
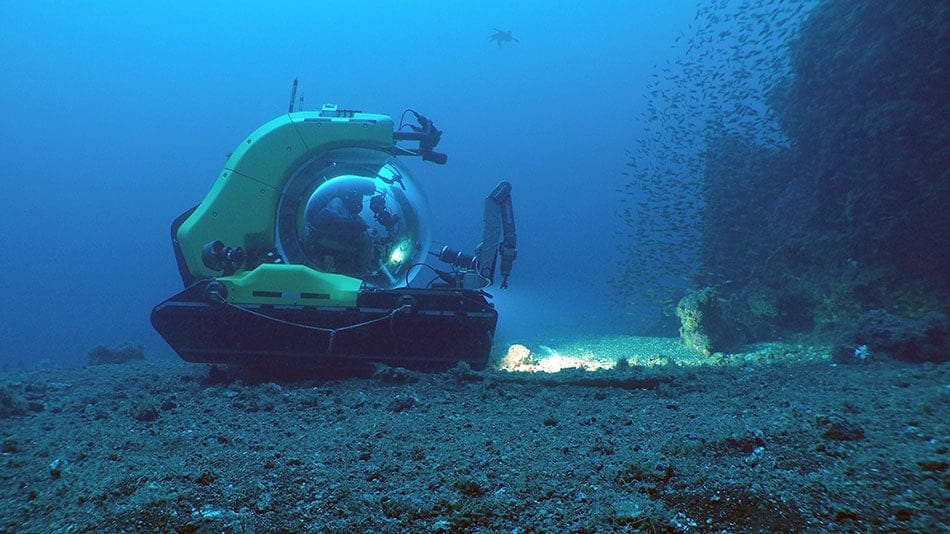
During a three-week expedition in August, an international team led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), in partnership with the Charles Darwin Foundation for the Galápagos Islands and in close collaboration with the Galápagos National Park Directorate, conducted the first scientific expedition to map and characterize the seamounts on the Galápagos platform and the diverse marine life that these underwater mountains support.
Read MoreHigher Levels of Fukushima Cesium Detected Offshore
Scientists monitoring the spread of radiation in the ocean from the Fukushima nuclear accident report finding an increased number of contaminated sites off the US West Coast, along with the highest detection level to date, from a sample collected about 1,600 miles west of San Francisco. The level of cesium in the sample is 50 percent higher than other samples collected, but is still more than 500 times lower than US government safety limits for drinking water and well below limits of concern for direct exposure while swimming, boating, or other recreational activities.
Ken Buesseler, a marine radiochemist with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and director of the WHOI Center for Marine and Environmental Radioactivity, was among the first to begin monitoring radiation in the Pacific, organizing a research expedition to the area just three months after the start of the ongoing accident. Through a citizen science sampling effort, Our Radioactive Ocean, as well as research funded by the National Science Foundation, Buesseler and his colleagues are using sophisticated sensors to measure minute levels of ocean-borne radioactivity from Fukushima. In 2015, they have added more than 50 new sample locations in the Pacific to the more than 200 previously collected and posted on the Our Radioactive Ocean web site.
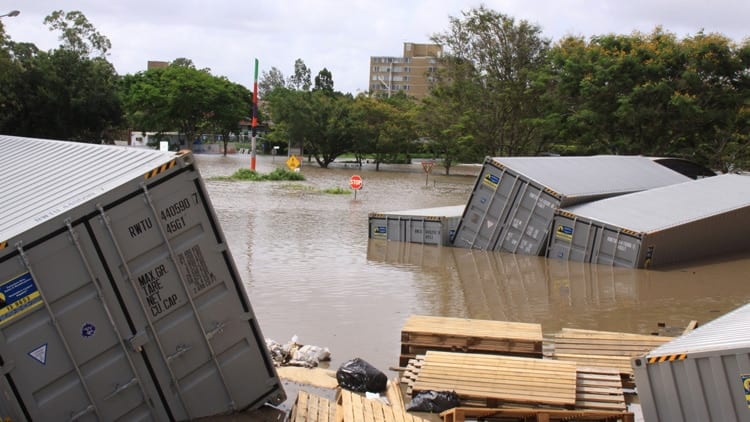
Read MoreWarming Ocean Worsened Australia’s Fatal 2010/2011 Floods
A study by a team of U.S. and Australian researchers shows that long-term warming of the Indian and Pacific oceans played an important role in increasing the severity of the devastating floods that struck Australia in 2010/2011. The study was published in Geophysical Research Letters.
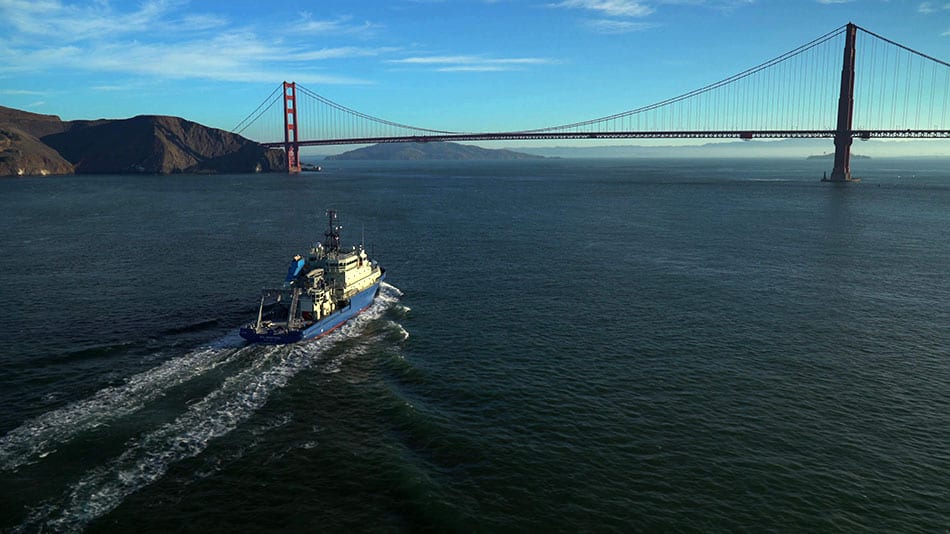
Read MoreSan Francisco Is First Port of Call for Nations Newest Research Ship
California welcomed the most recent addition to the US’s academic research fleet, the Neil Armstrong, as it made its first port of call in San Francisco over the weekend. The 238-ft., state-of-the-art ship made its way down the West Coast from Anacortes, Wash., where it was built.
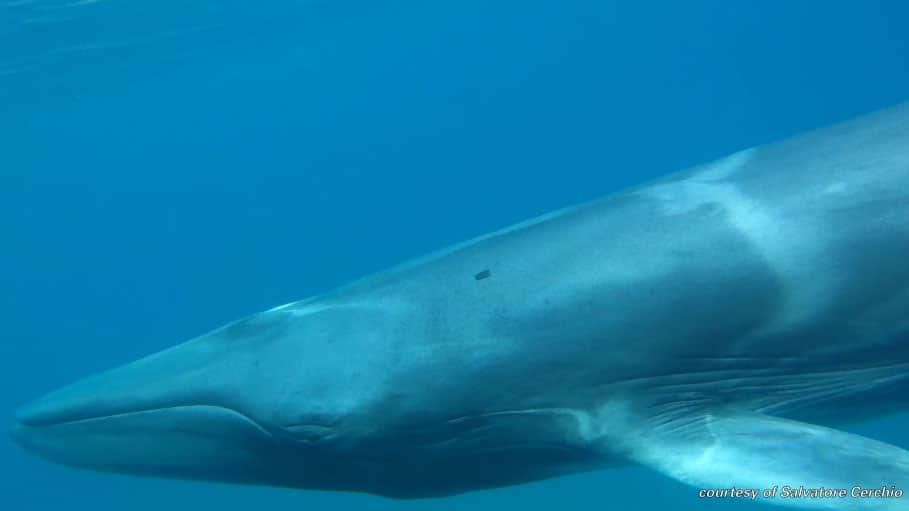
Read MoreNew Study Provides First Field Observations of Rare Omura’s Whales
In a paper published October 14, 2015, in the Royal Society Open Science journal, the researchers describe the whales’ foraging and vocal behaviors, and habitat preferences in the shallow waters of coastal Madagascar.
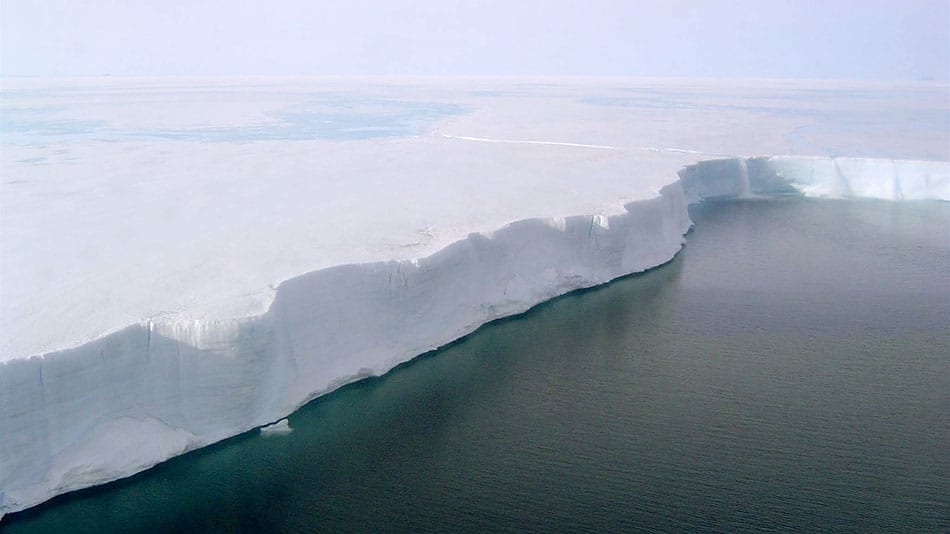
Read MoreNew Study Projects That Melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves Will Intensify
New research published today projects a doubling of surface melting of Antarctic ice shelves by 2050 and by 2100 may surpass intensities associated with ice shelf collapse, if greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel consumption continues at the present rate.
Ice shelves are the floating extensions of the continent’s massive land-based ice sheets. While the melting or breakup of floating ice shelves does not directly raise sea level, ice shelves do have a “door stop” effect: They slow the flow of ice from glaciers and ice sheets into the ocean, where it melts and raises sea levels.
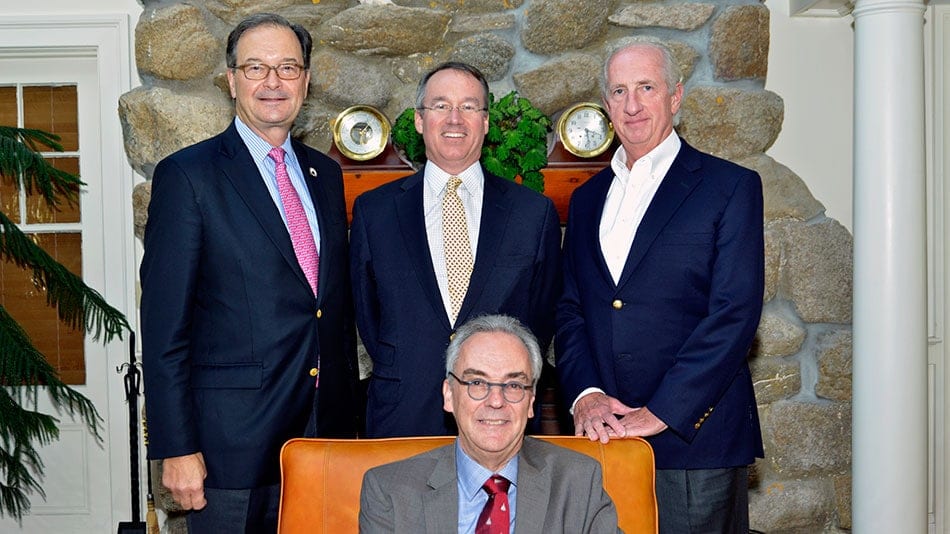
Read MoreWHOI Elects New Officers to its Board and Corporation
Today, the Board of Trustees of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) elected David B. Scully as the new chairman of the Board. Scully was elected to the WHOI Corporation in 2010 and to its Board in 2012. In addition to Scully’s appointment, Jefferson Hughes, Jr. has been elected vice chairman of the Board of Trustees, and Steven Hoch has been elected chairman of the WHOI Corporation.
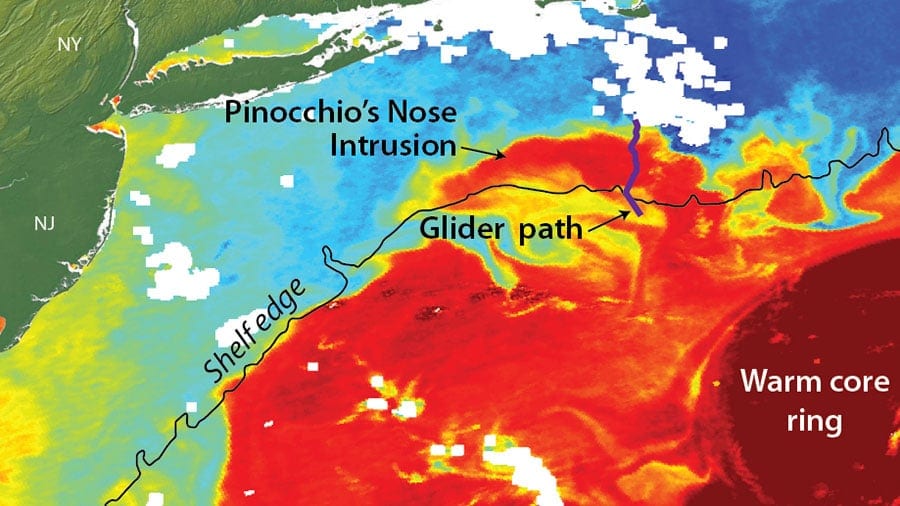
Read MoreGulf Stream Ring Water Intrudes onto Continental Shelf Like “Pinocchio’s Nose”
Ocean robots installed off the coast of Massachusetts have helped scientists understand a previously unknown process by which warm Gulf Stream water and colder waters of the continental shelf exchange. The process occurs when offshore waters, originating in the tropics, intrude onto the Mid-Atlantic Bight shelf and meet the waters originating in the Arctic. This process can greatly affect shelf circulation, biogeochemistry and fisheries.
In 2006, scientists using satellite imagery observed an elongated body of warm water from a Gulf Stream warm-core ring intruding along the shelf edge, extending hundreds of miles from Massachusetts towards Cape Hatteras, NC.
“A lot of people were surprised by this,” said Weifeng ‘Gordon’ Zhang, associate scientist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), and lead author of the study published [today] in Geophysical Research Letters. “Normally, the Gulf Stream water, which is very warm and buoyant, doesn’t come in direct contact with the water on the continental shelf, which is much colder. There is a cascade of potential implications that need further study.”
Read More
Novel Tag Developed for Squid, Jellyfish
A new data-logging tag, called the ITAG, developed at WHOI specifically for small and delicate invertebrates not only quantifies ocean conditions but also measures animals’ responses to their physical environments in high resolution.
Read MoreKing Crabs Threaten Antarctic Ecosystem Due to Warming Ocean
King crabs may soon become high-level predators in Antarctic marine ecosystems where they haven’t played a role in tens of millions of years, according to a new study led by […]
Read MoreWHOI Takes Delivery of New Research Vessel Neil Armstrong
Following completion of successful acceptance trials, the nation’s newest research vessel, the Neil Armstrong, was officially turned over by the U.S. Navy on September 23 to the Woods Hole Oceanographic […]
Read MoreMarine Archaeologists Excavate Greek Antikythera Shipwreck
Archaeologists excavating the famous ancient Greek shipwreck that yielded the Antikythera mechanism have recovered more than 50 items including a bronze armrest (possibly part of a throne), remains of a bone flute, fine glassware, luxury ceramics, a pawn from an ancient board game, and several elements of the ship itself.
“This shipwreck is far from exhausted,” reports project co-Director Dr. Brendan Foley, a marine archaeologist with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI). “Every single dive on it delivers fabulous finds, and reveals how the ‘1 percent’ lived in the time of Caesar.”
The shipwreck dates to circa 65 B.C., and was discovered by Greek sponge fishermen in 1900 off the southwestern Aegean island of Antikythera. They salvaged 36 marble statues of mythological heroes and gods; a life-sized bronze statue of an athlete; pieces of several more bronze sculptures; scores of luxury items; and skeletal remains of crew and passengers. The wreck also relinquished fragments of the world’s first computer: the Antikythera Mechanism, a geared mechanical device that encoded the movements of the planets and stars and predicted eclipses.
The 2015 expedition is part of a long-term research program at the site, which began in 2014. It was the first scientific excavation of the wreck, and launched the first comprehensive study of all of its artifacts. During the new multi-year program the team expects to recover artifacts and ancient artwork still buried in the seafloor, and recreate the history of the ship’s exquisite cargo and its final voyage.
Read MoreAssociated Industries of Massachusetts Honors WHOI
Associated Industries of Massachusetts (AIM) will honor the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) for contributions to the Massachusetts economy at an event Monday in Foxboro marking AIM’s centennial.
AIM will present its 100th anniversary Next Century award to WHOI, the world’s largest, private non-profit oceanographic research institution and a global leader in the study and exploration of the ocean. The award recognizes companies and institutions that have made unique contributions to the Massachusetts economy and the well-being of the people who live here.
Read MoreClimate Change Will Irreversibly Force Key Ocean Bacteria into Overdrive
A new study from University of Southern California and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) shows that changing conditions due to climate change could send Tricho into overdrive with no way to stop – reproducing faster and generating lots more nitrogen. Without the ability to slow down, however, Tricho has the potential to gobble up all its available resources, which could trigger die-offs of the microorganism and the higher organisms that depend on it.
Read MoreEvidence of Ancient Life Discovered in Mantle Rocks Deep Below the Seafloor
Ancient rocks harbored microbial life deep below the seafloor, reports a team of scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), Virginia Tech, and the University of Bremen. This new […]
Read MoreWHOI, NEAQ Embark on Expedition to the Phoenix Islands
A research team led by the New England Aquarium (NEAQ) and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) are heading out on a 6,000-mile expedition to one of the most remote places on Earth—the Phoenix Islands in the central Pacific Ocean. Throughout the month of September and in the midst of a strengthening Pacific El Nino, researchers will investigate the combined effects of climate change and human activity on the these vast coral reef ecosystems and the diversity of life they sustain.
Read MoreRhode Island Oceanographer, Professor Chosen to Receive Ketchum Award for Coastal Science
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has chosen Candace Oviatt, a professor of oceanography at the University of Rhode Island (URI), as the recipient of the 2015 Bostwick H. Ketchum Award.
Read MoreExamining the Fate of Fukushima Contaminants
An international research team reports results of a three-year study of sediment samples collected offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in a new paper published August 18, 2015, in the American Chemical Society’s journal, Environmental Science and Technology. The research aids in understanding what happens to Fukushima contaminants after they are buried on the seafloor off coastal Japan.
Read MoreNew AUV Plankton Sampling System Deployed
Traditionally, pumps and nets are used for sampling plankton, which require sampling at predetermined stations or towing nets behind a ship, followed by visually sorting collected organisms into taxonomic groups. Samples generally combine organisms collected throughout horizontal or vertical tracks, making it impossible to detect small gradations or species-specific patterns in larval distribution.
The sampling system combines three cutting edge technologies—an adapted Suspended Particulate Rosette (SUPR) multi-sampler, a REMUS autonomous underwater vehicle equipped with sensors, and identification of organisms by DNA barcode analysis. They’ve dubbed the new system “SUPR-REMUS.”
Read MoreHeat Release from Stagnant Deep Sea Helped End Last Ice Age
The build-up and subsequent release of warm, stagnant water from the deep Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas played a role in ending the last Ice Age within the Arctic region, according to new research led by an international team of scientists.
The study, published today in Science, examines how the circulation of the combined Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas – called the Arctic Mediterranean – changed since the end of the last Ice Age (~20,000-30,000 years ago). The results highlight the important impact that changes in ocean circulation can have on climate.
Read MoreUltrasounds for Coral Reefs?
In a study, published Aug. 6, 2015 in Marine Ecology Progress Series, scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) used low-cost autonomous underwater recorders over four months to collect “soundscapes” of reefs in in the U.S. Virgin Islands. They showed how the collective sound recordings of reef inhabitants painted vivid pictures of the reefs’ abundance and diversity.
In a second study, published the same day in Marine Pollution Bulletin, the researchers recorded boat noise—showing how it could mask vital sounds that organisms make to reproduce, feed, and find new homes. They also demonstrated how underwater recorders could help marine managers keep an ear on potentially disruptive human activity in far-off locations.
Read MoreRiver Buries Permafrost Carbon at Sea
As temperatures rise, some of the carbon dioxide stored in Arctic permafrost meets an unexpected fate—burial at sea. As many as 2.2 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) per year are swept along by a single river system into Arctic Ocean sediment, according to a new study led by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) researchers and published today in Nature. This process locks away the greenhouse gas and helps stabilize the earth’s CO2 levels over time, and it may help scientists better predict how natural carbon cycles will interplay with the surge of CO2 emissions due to human activities.
“The erosion of permafrost carbon is very significant,” says WHOI Associate Scientist Valier Galy, a co-author of the study. “Over thousands of years, this process is sequestering CO2 away from the atmosphere in a way that amounts to fairly large carbon stocks. If we can understand how this process works, we can predict how it will respond as the climate changes.”
Permafrost—the permanently frozen ground found in the Arctic and Antarctic and in some alpine regions—is known to hold billions of tons of organic material, including vast stores of CO2. Amid concerns about rising Arctic temperatures and their impact on permafrost, many researchers have directed their efforts to studying the permafrost carbon cycle—the processes through which the carbon circulates between the atmosphere, the soil and surface (the biosphere), and the sea. Yet how this cycle works and how it responds to the warming, changing climate remains poorly understood.
Galy and his colleagues from Durham University, the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, the NERC Radiocarbon Facility, Stockholm University, and the Universite Paris-Sud set out to characterize the carbon cycle in one particular piece of the Arctic landscape—northern Canada’s Mackenzie River, the largest river flowing into the Arctic Ocean from North America and that ocean’s greatest source of sediment. The researchers hypothesized that the Mackenzie’s muddy water might erode thawing permafrost along its path and wash that biosphere-derived material and the CO2 within it into the ocean, preventing the release of that CO2 into the atmosphere.
Read MoreShifting Winds, Ocean Currents Doubled Endangered Galapagos Penguin Population
New research suggests shifts in wind currents over the past three decades, possibly due to climate change and natural variability, have nudged the Equatorial Undercurrent north. The changing current expanded the nutrient-rich, cold water farther north along the coasts of the two islands, likely bolstering algae and fish numbers in the cold pool. This allowed the penguin population to double over the past 30 years, swelling to more than 1,000 birds by 2014, according to the new study.
Read MoreWhale Research Takes Flight
A research team has successfully demonstrated a new non-invasive tool to obtain hard-to-get health measurements of large endangered whales in the wild: Using a small remote-controlled hexacopter, scientists for the first time collected both breath samples from the whales’ spouts combined with aerial photos of their body condition.
Read More