Research Highlights
Oceanus Magazine
News Releases
A new study investigates how the influence of low gravity, as found on ocean worlds in our solar system, impacts flow of water and heat below their seafloors.
MIT, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution researchers find wave activity on Saturn’s largest moon may be strong enough to erode the coastlines of lakes and seas.
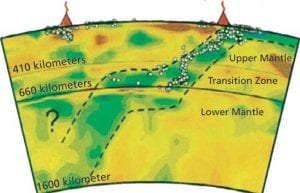
Ocean scientists discovered the new deep-sea hydrothermal vent sites on the seafloor at 2,550 meters (8366 feet, or 1.6 miles) depth.
Woods Hole, MA – A team of scientists led by a Tulane University oceanographer and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has found that deposits deep under the ocean floor reveal a way to measure the ocean oxygen level and […]
Woods Hole, Mass. -Evidence of climate change in the North Atlantic during the last 1,000 years can be seen in the deep ocean, according to a newly published paper led by researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and […]
News & Insights
This week, NASA’s Perseverance Rover lands on Mars to continue the search for life on the Red Planet. At the same time, WHOI scientists and engineers are applying their experience exploring the deepest parts of planet Earth to the quest […]
As glaciers melt at unprecedented rates, WHOI’s Simon Pendleton is looking back to historical records to predict whether this new cool runoff will slow ocean circulation and cool the northern hemisphere––findings which could mean adjustments to some climate predictions.