Research Highlights
Oceanus Magazine
Danielle Haas Freeman draws on the language of chemistry to solve an oil spill puzzle
News Releases
A new report from researchers at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) reveals for the first time the unseen—and somewhat surprising—benefits that people receive from the ocean’s twilight zone. Also known as the “mesopelagic,” this is the ocean layer just beyond the sunlit surface.
A collaborative study compared seawater from 25 reefs in Cuba and the U.S. Florida Keys varying in human impact and protection, and found that those with higher microbial diversity and lower concentrations of nutrients and organic carbon—primarily caused by human activities—were markedly healthier.
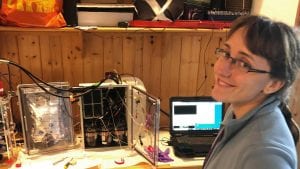
WHOI researchers successfully conceived and tested a portable device, DISCO, that performed the first in situ measurements of a highly reactive type of oxygen, known as superoxide, which may play an integral role in the health of coral reefs.
WHOI scientists distinct discover microbes living just a few centimeters from the surface of corals near the southern coast of Cuba. The discovery may yield clues about the ecological functions of microbes, and how they find and infect coral colonies.
Two years ago an international team of scientists visited Costa Rica’s subduction zone, where the ocean floor sinks beneath the continent and volcanoes tower above the surface. They wanted to find out if microbes can affect the cycle of carbon…